39 fungal life cycle diagram
The life cycle of an ascomycete is characterized by the production of asci during the sexual phase. The haploid phase is the predominant phase of the life cycle. The Basidiomycota (basidiomycetes) are fungi that have basidia (club-shaped structures) that produce basidiospores (spores produced through budding) within fruiting bodies called ... Yeast is an example of a single-celled fungus. Fungal cell structure Fungal cells have a cell wall made of chitin (remember that plant cell walls are made of cellulose).
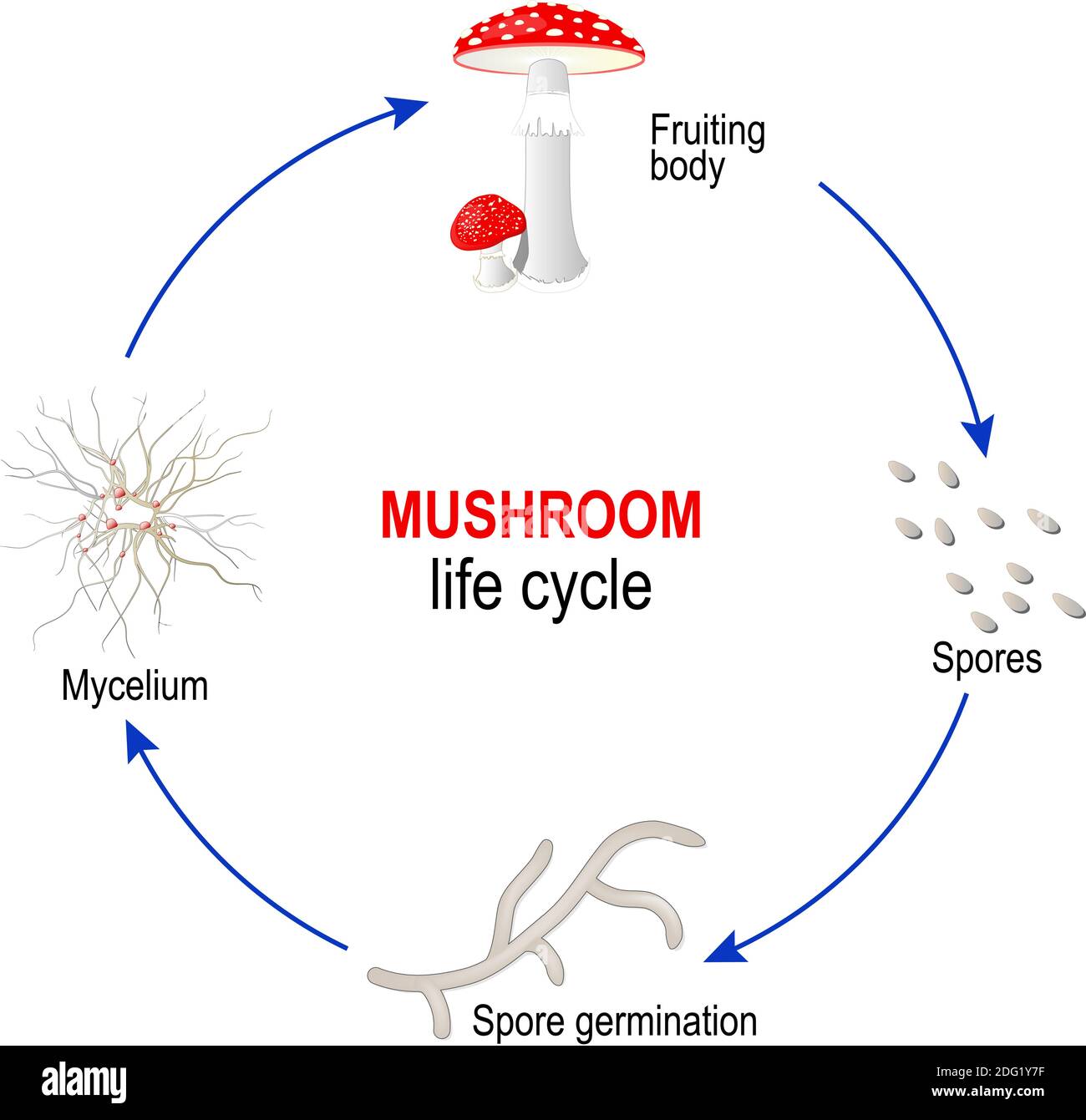
The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould.

Fungal life cycle diagram
II. LIFE CYCLE OF A 'TYPICAL' FUNGUS. Generalized Life Cycle of Fungi. REFER TO DIAGRAM FROM CLASS NOTES OR TO THE FOLLOWING: . Also visit the following links for additional information: Review this diagram of the moss life cycle from the video. The moss life cycle consisting of 5 stages. The following structures are labeled clockwise: spores, gametophyte, egg, zygote, and sporophyte. The two labels indicate specific events in the life cycle. Fertilization is between the structures labeled egg and zygote. Fungi are found everywhere from the air, soil, river, lakes and seas to plants, animals, clothing, etc. Let's look at the life cycle of fungi to get a better understanding. Life Cycle of Fungi: The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way.
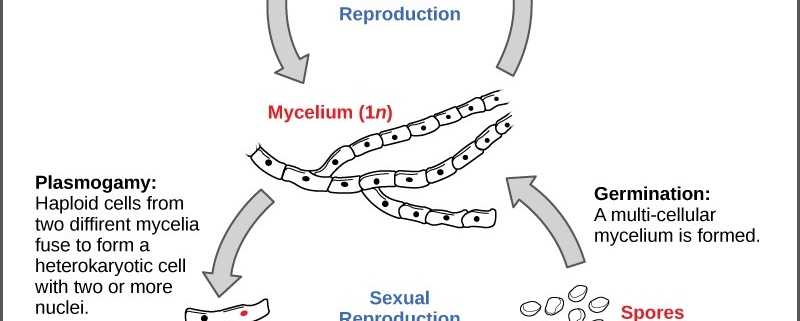
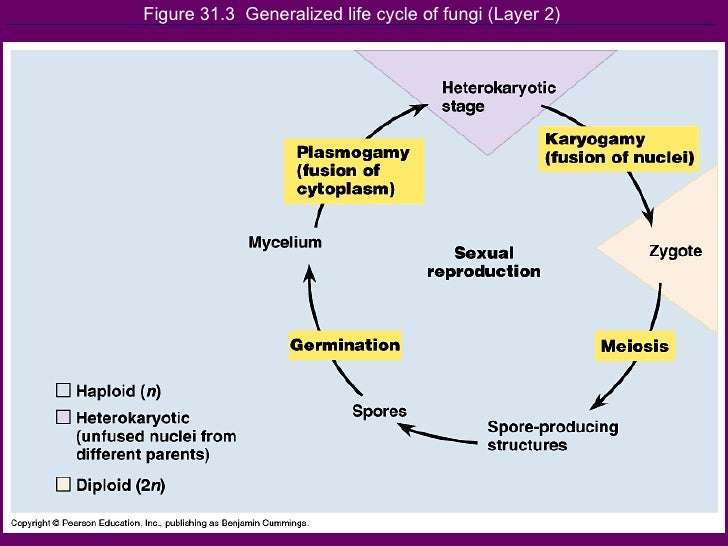
Fungal life cycle diagram. • example of fungal life cycle with dikaryotic hyphae: mushroom dikaryotic mycelium is major phase only when mushroom is formed does karyogamy occur, followed by meiosis Complete the life cycle to explain the generalized life cycle of fungi (use textbook Figure 31.5): D. Fungal phylogeny Five phyla plus "imperfect fungi" ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of penicillium with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Penicillium: The mycelium is well developed and copiously branched. It is composed of colourless, slender, tubular, branched and septate hyphae. The hyphae run in all directions on the substratum and become intertwined with one […] The basic life cycle of Fungi--You can edit this template on Creately's Visual Workspace to get started quickly.Adapt it to suit your needs by changing text and adding colors, icons, and other design elements. Easily export it in PNG, SVG, PDF, or JPEG image formats for presentations, publishing, and printouts. In the gametic life cycle, the gamete (egg or sperm) is the only haploid cell produced. meiosis fertilization mitosis 2n multicelled -----> 1n gamete -----> 2n zygote -----> 2n multicelled Fungi Kingdom: Zygotic Life Cycle In the zygotic life cycle, the zygote is the only diploid cell produced.
The life cycle of fungi has a wide range of examples dependent on the types of the fungi. Not all fungi imitate similarly. While a few fungi recreate sexually, others duplicate asexually. Hence, we are going to take a gander at the life cycle of fungi in the asexual and sexual stage. Spores produced by mature fungi are released into the surrounding environment, where they divide and grow into hyphae. Hyphae are root-like threads composed of ... A symbiotic fungus that forms sheaths of hyphae over the surface of plant roots and also grows into extracellular spaces of the root cortex. Label the features of a general fungal life cycle with the correct descriptions. Life cycle of fungi in the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of aspergillus with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Aspergillus: It is well developed and made up of a loosely interwoven mass of hyaline, bright or pale coloured, extensively branched, septate hyphae. Some of the hyphae ramify superficially upon the substratum. Others penetrate […]
Fungal life cycles - spores and more. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. Some fungi are multicellular, while others, such as yeasts, are unicellular. Most fungi are microscopic, but many produce the visible fruitbodies we call mushrooms. Fungi can reproduce asexually by budding, and many also have sexual ... The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. fungus - fungus - Life cycle of fungi: In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus, a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion, and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote (the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells). Meiosis (reduction division) restores the haploid number of chromosomes and ... Regardless of the method of reproduction, most indoor mold follows the following asexual life-cycle pattern: 1. Hyphae Growth. The hypha are the cells that start the life-cycle process. Hypha(e) are cellular strands that release digestive enzymes that help to decompose substrate for nutrition.
A thick, black protective coat forms around the zygotes during sexual reproducation. meiosis occurs during zygosporezygosporeA zygospore is a diploid reproductive stage in the life cycle of many fungi and protists. In fungi, a sporangium is produced at the end of a sporangiophore that sheds spores. A fungus that forms zygospores is called a ...
of spore-producing structures, and one diploid cell in the life cycle! Multicellular Fungal Life Cycles. Typical Examination Questions 1. Describe the unique and common features of named fungal groups. 2. Describe the various reproductive life cycles associated with fungi.
Nov 1, 2013 — Filamentous fungi begin their lives as sexual spores. Each spore has a haploid (only one copy of each chromosome) nucleus, ...
Description
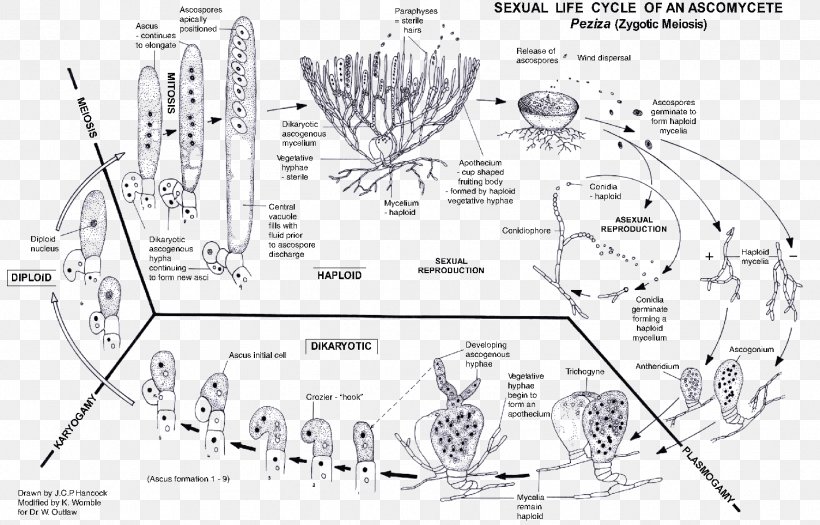
Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Sac Fungi Biological Life Cycle Mycelium Png 1505x965px Mycorrhiza Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Area Artwork Asexual
Macroscopic fungi such as morels, mushrooms, puffballs, and the cultivated agarics available in grocery stores represent only a small fraction of the diversity in the kingdom Fungi. The molds, for example, are a large group of microscopic fungi that include many of the economically important plant parasites, allergenic species, and opportunistic pathogens of humans and other animals. They are ...
Yeast: morphology and life cycle. They are single celled fungi; Size: generally larger than most bacteria; (1-5) um wide and (5-30)um length Shape: cell is egg shaped, some are elongated or spherical Size and shape varies among species; Yeast cell lacks flagella and other organ of locomotion.
The diagram below shows the generalized life cycle of fungi. Spores are reproductive cells that are dispersed by wind. They are capable of germinating and producing a new mycelium. Ecology: Some Important Symbiotic Relationships . Lichens
The life cycle of a fungus is divided into two parts, called anamorphic and teleomorphic stages. During the anamorphic stage, the fungus is able to reproduce asexually. The teleomorphic stage is known as the fruiting stage. It is defined by the organism's ability to reproduce sexually. When referring to a fungus including both of these stages ...
Life cycle in Wheat • Wheat is the primary host upon which dikaryophase of the pathogen is completed • This phase consists of well developed branched, septate, dikaryotic vegetative mycelium and two spore stages namely, uridenial stage and telial stage.
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms. ... The following description of the characteristics of Basidiomycota traces the life cycle of a "typical" species, beginning at the site of meiosis. ... Assembling the Fungal Tree of Life. Collaborative research in fungal phylogenetics.
The first phase of the fungal life cycle is the spore phase. All fungi begin as spores that are 'haploid,' meaning they only have one copy of all their genetic information. This is similar to human sex cells, like sperm and eggs. These spores can travel vast distances from where they were produced by hitching a ride on another organism or ...
Fungi are found everywhere from the air, soil, river, lakes and seas to plants, animals, clothing, etc. Let's look at the life cycle of fungi to get a better understanding. Life Cycle of Fungi: The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way.
Review this diagram of the moss life cycle from the video. The moss life cycle consisting of 5 stages. The following structures are labeled clockwise: spores, gametophyte, egg, zygote, and sporophyte. The two labels indicate specific events in the life cycle. Fertilization is between the structures labeled egg and zygote.
II. LIFE CYCLE OF A 'TYPICAL' FUNGUS. Generalized Life Cycle of Fungi. REFER TO DIAGRAM FROM CLASS NOTES OR TO THE FOLLOWING: . Also visit the following links for additional information:
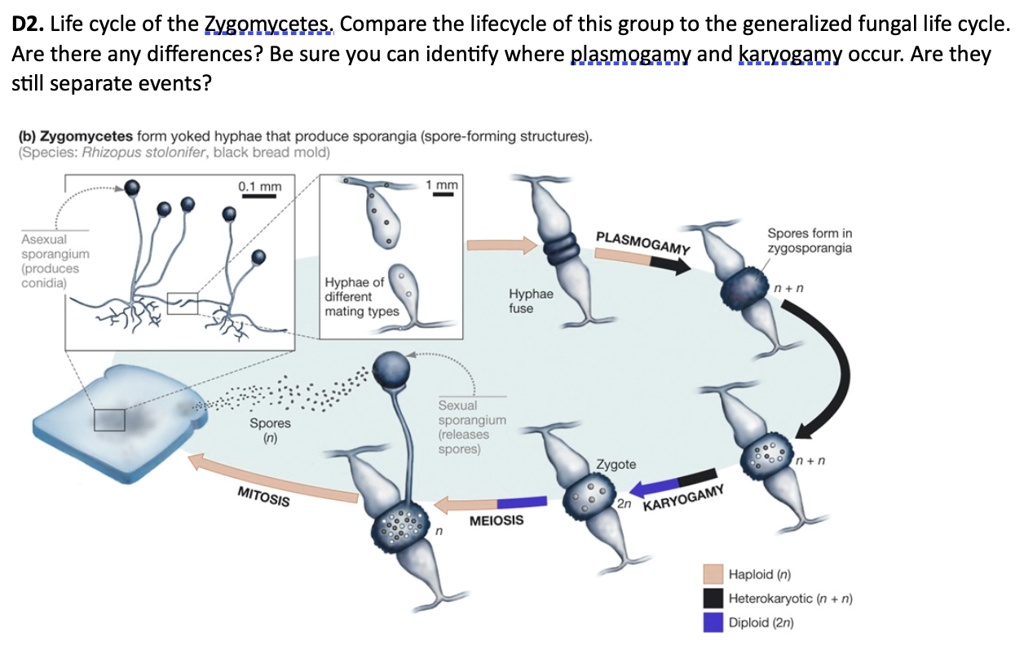
Solved D2 Life Cycle Of The Zygomycetes Compare The Lifecycle Of This Group To The Generalized Fungal Life Cycle Are There Any Differences Be Sure You Can Identify Where Plasmogamy And Karyogamy Occur
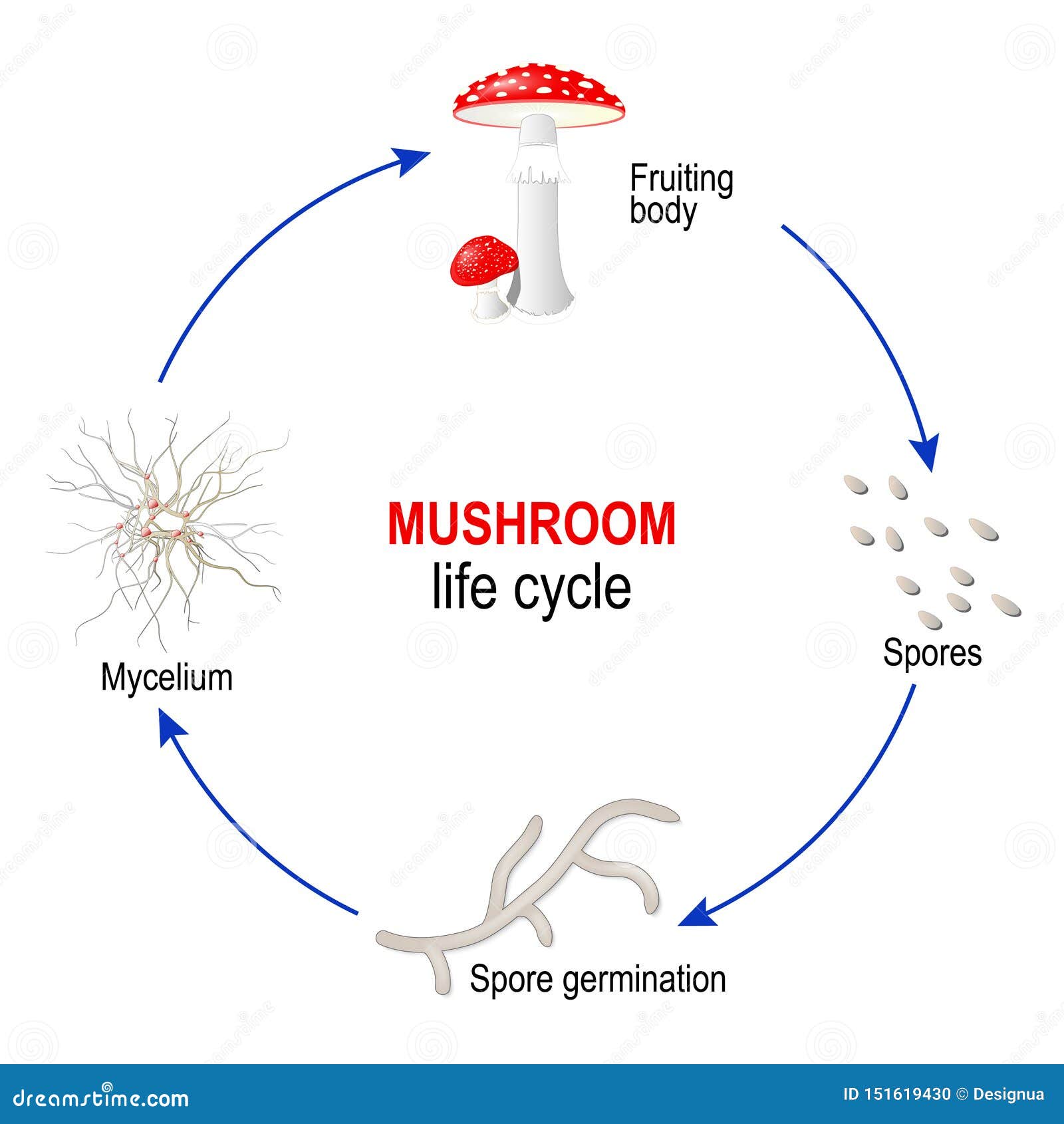
Mushroom Life Cycle From Spores To Mycelium And Fungi Fruiting Body Amanita Muscaria Stock Vector Illustration Of Background Macro 151619430




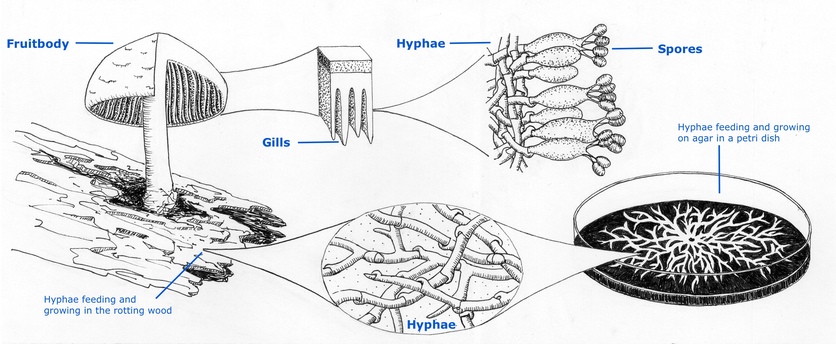



.png?revision=1)








.png?revision=1)

Comments
Post a Comment