40 monocot leaf diagram
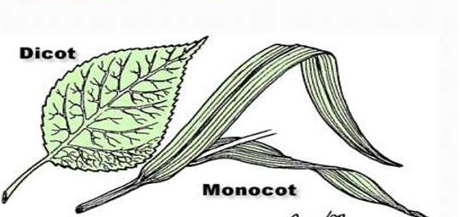
› parts-of-a-leafParts of a Leaf, Their Structure and Functions With Diagram Jul 03, 2020 · A leaf is a plant organ that is flat, thin and usually green in color. It is mostly found above the ground and remains attached to the stem.. The presence of pigment ‘chlorophyll’ makes the leaf green in color that helps to prepare food in plants through photosynthesis. How is a typical monocot leaf attached to the stem MAKE A ... Monocots have one cotyledon (vein)w whereas dicots have two. Some leaves are attached to the plant stem by a petiole. Leaves that do not have a petiole and are directly attached to the plant stem are called sessile leaves. Monocots have parallel venation in which the veins run in straight lines across the length of the leaf without converging.
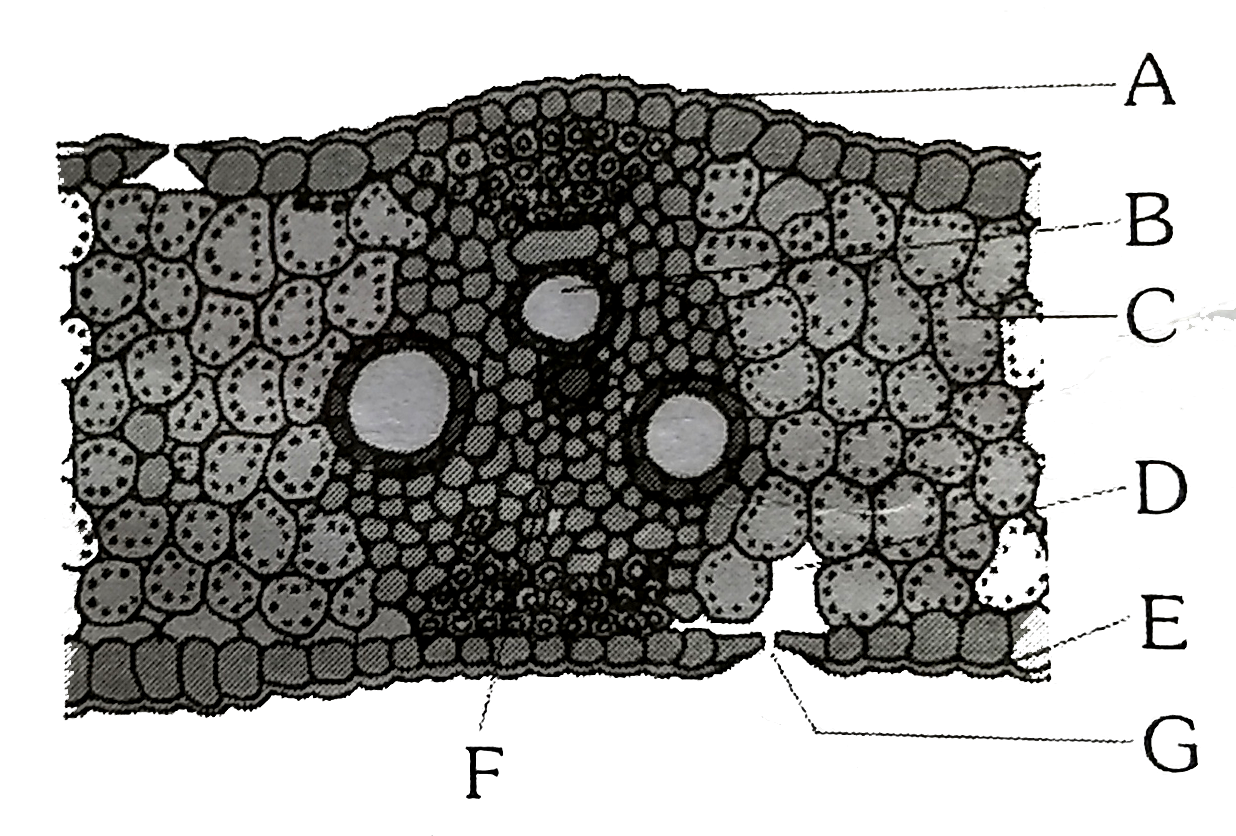
Solved Q 14. In the diagrams below identify the cross ... In the diagrams below identify the cross section of monocot and dicot leaf? 2 Points b. Q.15. Identify each of the structures in the micrograph of a monocot stem below by using the appropriate choices from the list. 4 Points xylem, phloem, parenchyma, epidermis C Q. 16.
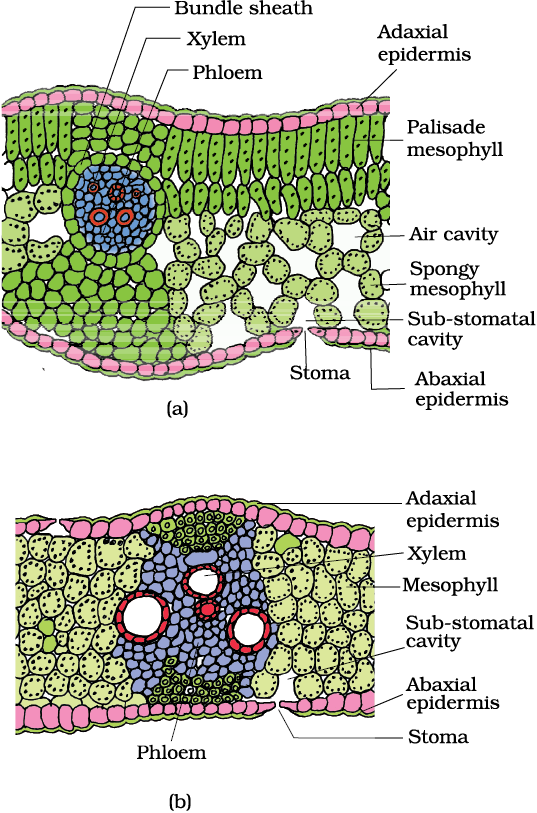
Monocot leaf diagram
Explore the Difference Between Monocot and Dicot leaf Difference Between Monocot Leaf and Dicot Leaf Historically, plants are classified into two categories based on the number of cotyledons or embryonic leaves. Therefore, the term "monocot" refers to the flowering plants that contain only one cotyledon. Stem Anatomy || Monocot and Dicot Stem Cross Section In this tutorial, we have described Stem Anatomy (Monocot and Dicot Stem Cross Section). DICOT STEM CROSS SECTION For studying the internal structure of a typical dicot stem, the stem cross section of a young Sunflower or Cucurbita is taken. A thin transverse section of the stem reveals the following structures under the microscope: 1. Epidermis It forms a single and the outermost layer of the ... study.com › academy › lessonMonocot: Definition, Function & Examples - Video & Lesson ... Aug 29, 2021 · A monocot is a plant with one seed leaf, referred to as cotyledon. Learn the more extensive definition of monocot through exploring examples of cotyledon and its function in the ecological system.
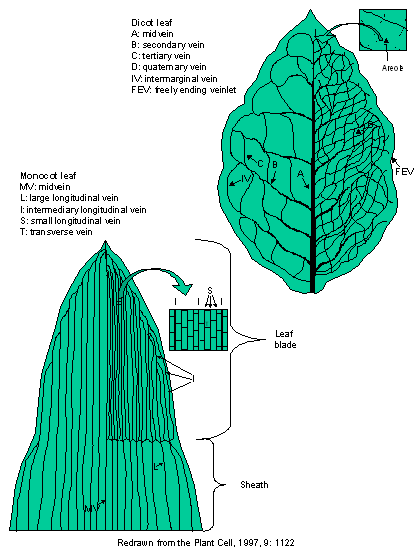
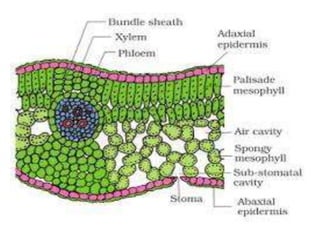
Monocot leaf diagram. ncert.nic.in › pdf › publicationII - NCERT 8. Draw the diagram of a stoma and label its parts. 9. Repeat the process with peels removed from a monocot leaf. Record your observations. 10. Following the same procedure, study the stomata of other dicot and monocot plants. OBSERVATIONS Sl. No. Observation Dicot Monocot 1. Number of stomata in the microscopic field 2. Of The Best Diagram Of A Leaf - Glaucoma Template External Anatomy Of The Stem. A leaf diagram representing the parts of a leaf. Diagram Of A Monocot Leaf Hibiscus Leaves Leaves Diagram. Cross section of Leaf Diagram Class 10 BiologyHi friends In this video we will learn How to Draw Cross section of Leaf. 1 petiole 2 leaf base and 3 leaf blade or lamina each performing specific functions. PDF Dicot or Monocot? How to Tell the Difference - USDA base of the leaf and are parallel to each other in each lobe of the leaf. If your plant is flowering, you can tell if it is a monocot or dicot by the number of petals and other flower parts. Monocots have flower parts in threes or multiples of threes as shown in the flowers to the left. Dicots have flower parts in multiples of fours or fives like Difference Between Dicot and Monocot Leaf - Biology Reader The monocot leaves are generally linear or oblong and the vascular bundles in them are parallel arranged in the striated veins. These are amphistomatous, i.e. possess stomata on both the sides (upper and lower epidermis) and have striate venation. Here, the mesophyll is undifferentiated. Diagram
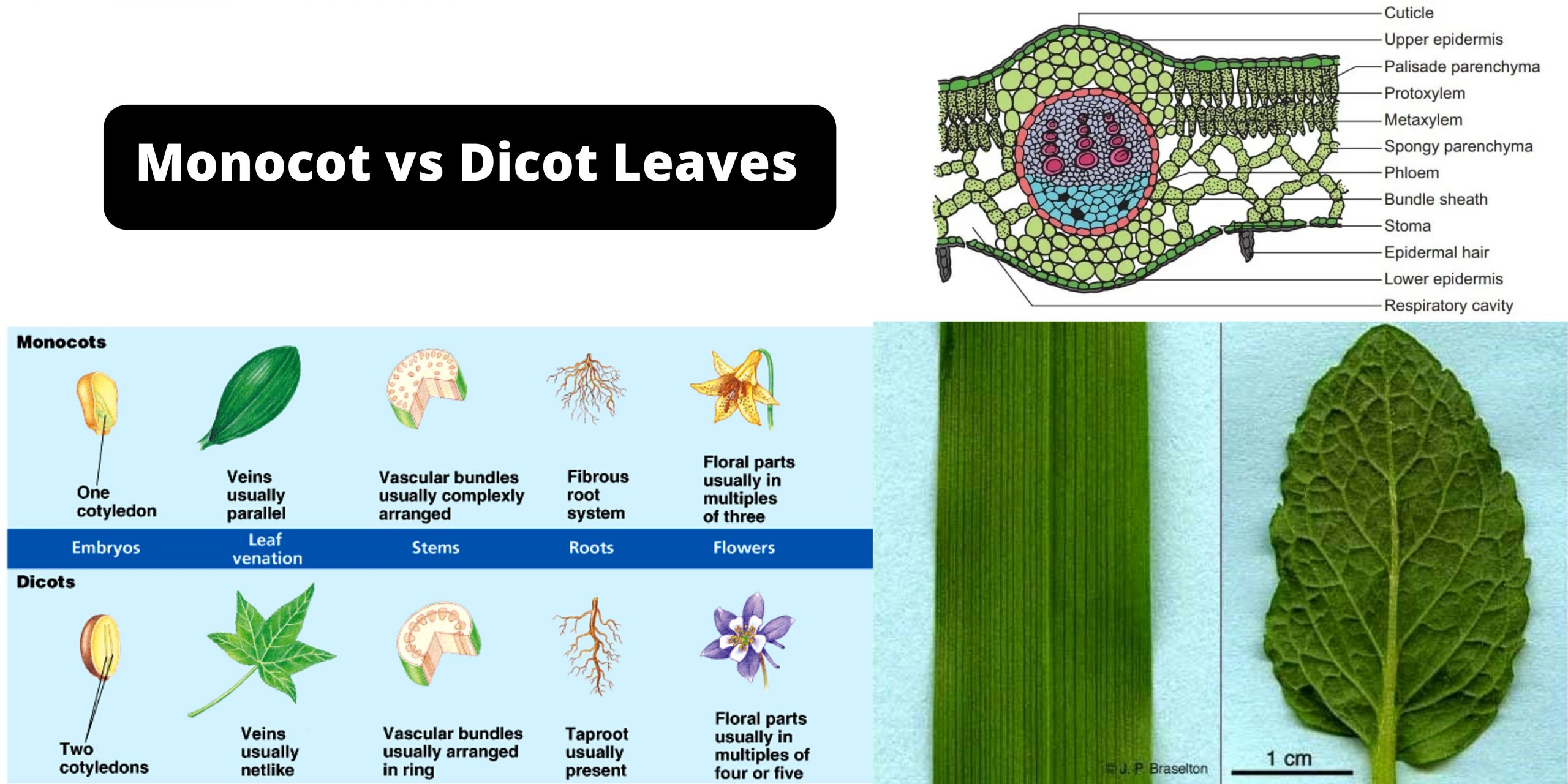
PDF Diagrams Of Monocot Leaf Under The Microscope diagrams of monocot leaf under the microscope std xi science biology practical handbook. dictionary com s list of every word of the year. photosynthesis wikipedia. mader biology 10 e - chapter outlines. a d american phytopathological society. physiology of flowering grkraj org. biology biol lt 1 / 5 Anatomy of Leaf: Meaning, Diagrams, Types, and Comparison The mesophyll is differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma in the dicot leaf but not in the monocot leaf. The vascular bundle is scattered and of different sizes; due to reticulate venation in the dicot leaf and monocot leaf, vascular bundles are nearly similar due to the presence of parallel venation. Describe the T.S. of monocot and dicot leaf with the ... Monocot's leaf or isobilateral leaf. Most of the monocot leaves are nearly erect and more or less both surfaces usually receive a direct and equal amount of sunlight. The internal structure of the monocot leaf shows the following anatomical structure. Epidermis: The epidermis is found on both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf. Monocots vs. Dicots, With Diagrams - Plants Grow Here Diagram via Plants Grow Here. Leaf Veins Monocots tend to have parallel leaf veins (or venation), where the veins run parallel from the leaf stem (or petiole) to the tip, as seen on a blade of grass. Dicots tend to have reticulate leaf venation, where the veins branch off and laterally.
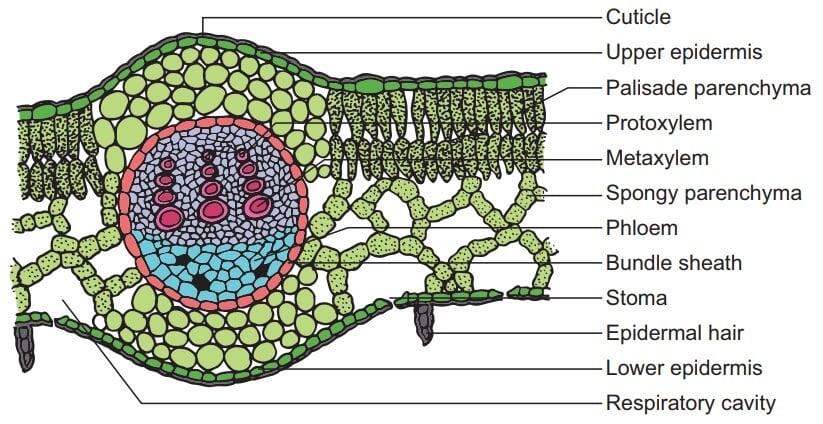
Internal Structure of Leaf: Parts, Function, Diagram - Embibe Fig: T.S of Leaf (a) Dicot and (b) Monocot. Summary. A leaf is a flattened appendage on the stem which is born in the node. The internal structure of the leaf tells us about the arrangement of the different cells or tissues. Typically the internal structure of leaves comprises the upper epidermis and lower epidermis encompassing the mesophyll cell. Monocot Diagram - schematron.org This article provides a diagram of monocot root. Also learn about: 1. Portion of transverse section of monocot root (arum) showing the plan of arrangement of. Monocotyledons commonly referred to as monocots are flowering plants ( angiosperms) whose seeds typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. Monocot Leaf Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Monocot Leaf. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Weeds: Monocot - CropWatch Illustrated diagram of the differences of Monocot and Dicot plant anatomy: Embryos, Leaf Ventilation, Flowers, Stems, and Roots. Monocot Careful attention to detail is critical in proper identification as each step in the key is evaluated.
Monocot and Dicot Leafs (With Diagram) | Plants ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top two types of monocot and dicot leafs. The types are: 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf 2. Anatomy of Dicot Leaf. Monocot and Dicot Leaf: Type # 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf: Triticum-Leaf: ADVERTISEMENTS: T.S. shows prominent ridges and grooves and reveals the following tissues: Epidermis: 1. Two epidermal […]
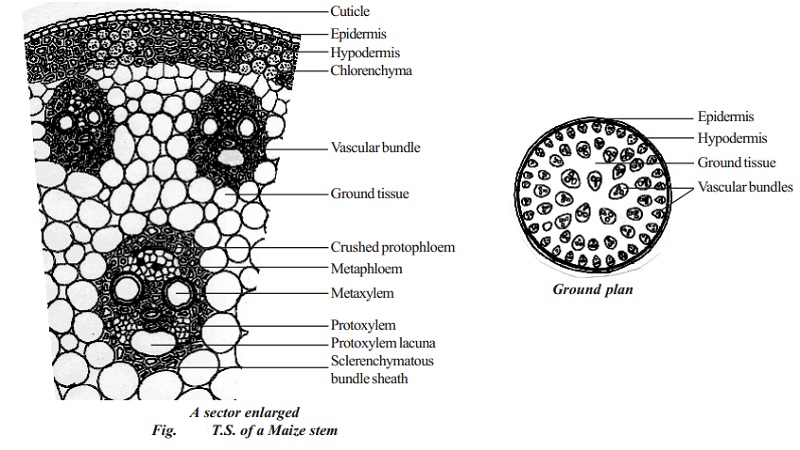
Difference Between Monocot and Dicot Stem: Diagrams ... The below diagram of the Transverse Section of Monocot stem will provide a clear understanding of its major components. ... Ans: To differentiate between a monocot and a Dicot plant, some of the characteristics include leaf venations, number of cotyledons, root system and others. Parameter Monocotyledon Dicotyledon;
Diagram Of A Monocot Leaf | Hibiscus leaves, Diagram, Leaves Diagram Of A Monocot Leaf. Find this Pin and more on Leaves by Linaee Marx. Hibiscus Leaves. Hd Background Download. The Diagram. Leaf Images. Leaf Drawing. Hd Backgrounds. Image Search.
Labeled Monocot Plant Diagram - Diagram Sketch Labeled Monocot Plant Diagram. angelo on February 2, 2022. Monocot Germination Corn Seedling Photo Biology Plants Plant Science Germination. Diagram Of A Monocot Leaf Hibiscus Leaves Leaves Diagram. Parts Of A Plant Worksheet Find A Flower To Dissect And Glue Appropriate Parts To Sheet Parts Of A Flower Plants Worksheets Plant Lessons.
Diagram Of Transverse Section A Dicot Leaf | Leafandtrees.org Difference Between Dicot And Monocot Leaf With Comparison Chart Biology Reader. Schematic transverse section through a dicotyledon leaf indicating the scientific diagram monocot and dicot leafs with diagram plants 3 dorsiventral cross section of a dicot leaf with the adaxial surface scientific diagram monocot and dicot leafs with diagram plants.
genomebiology.biomedcentral.com › articles › 10High-quality reference genome sequences of two coconut ... Nov 04, 2021 · Background Coconut is an important tropical oil and fruit crop whose evolutionary position renders it a fantastic species for the investigation of the evolution of monocot chromosomes and the subsequent differentiation of ancient plants. Results Here, we report the assembly and annotation of reference-grade genomes of Cn. tall and Cn. dwarf, whose genome sizes are 2.40 Gb and 2.39 Gb ...
Monocot Root Cross Section Structure (with PPT) | Easy ... Anatomy of Monocot Root (Monocot Root Cross Section Under Microscope with Diagram) Ø The anatomical features of a monocot root can be studied through a cross section (CS) through the root. Ø Anatomically, the monocot root has been differentiated into the following parts: (1). Epidermis (2). Cortex (3). Endodermis (4). Pericycle (5).
byjus.com › biology › preparation-and-study-ofPreparation And Study Of T.S Of Dicot And Monocot Roots And ... Diagram. T.S Of Dicot Stem. T.S Of Monocot Stem. Procedure Taking Sections. Hold the dissected plant material between your index finger and thumb, while keeping the edge of the razor perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the plant. Slice it into thin sections. Using the edge of the blade, shift these sections into a watch glass with the ...
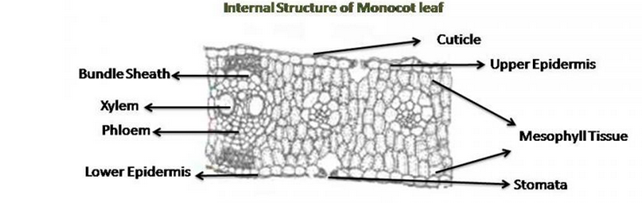
Internal Structure of Monocot Leaf | Definition, Examples ... A transverse section passing through the midrib region of an iso-bilateral leaf (maize) reveals the following structure. ... Internal Structure of Monocot Leaf. ... Describe the internal structure of dicot leaf with the help of diagram. Hard. View solution > In a dicot root vascular cambium is. Hard.
Roots, Stems and Leaves Diagrams - Mandeville High School Roots, Stems and Leaves Diagrams. External Root Structure. Monocot Root. Dicot Root. External Structure of a Woody Stem. Monocot Stem. Woody Dicot Stem. Monocot Leaf. Dicot Leaf.
Monocot And Dicot Plants- Anatomy - BYJUS Monocot roots do not show much difference in the anatomy from that of the dicot roots. Monocot plants possess an adventitious root system. As in the dicots, the epidermis forms the outermost layer, followed by cortex, pericycle, endodermis, vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) and pith (random order).
study.com › academy › lessonClassification of Vascular, Nonvascular, Monocot & Dicot ... Aug 22, 2021 · A flowering plant is either considered to be a monocot or a dicot. Let's first look at monocots. Let's first look at monocots. Monocot is short for 'monocotyledon,' meaning 'one seed leaf.'
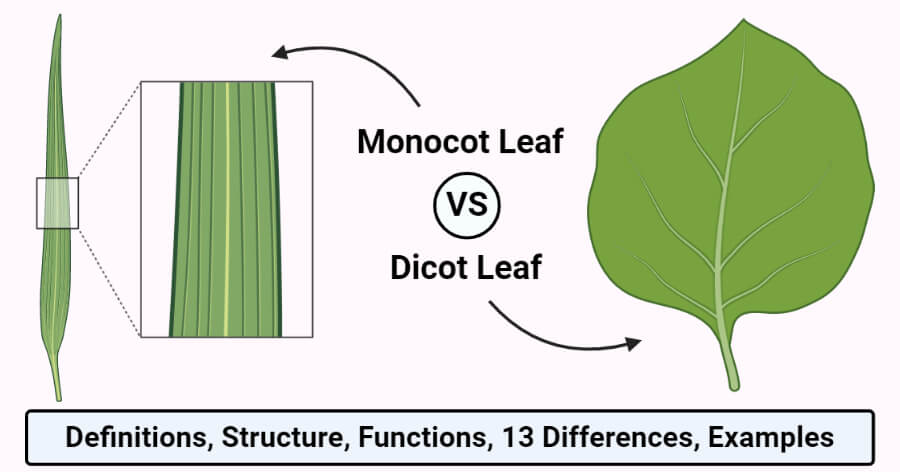
16 Difference Between Monocot And Dicot Leaf With Examples ... Leaf is the main place where photosynthesis occurs. Most leaves are usually green, due to presence of chlorophyll in the leaf cells. However, some leaves may have different colors, caused by other plant pigments that mask the green chlorophyll. In this article, learn the difference between monocot and dicot leaves. The basis of comparison include: […]
labs.plb.ucdavis.edu › courses › bisChapter 5 The Shoot System I: The Stem have one leaf per node, and the angle of divergence between leaves is 137.5° (Fig. 5.6d). Primary Growth Differs in Monocot and Dicot Stems Monocot stems differ in several ways from the patterns described for dicot stems. One main difference is that the vascular bundles tend to be scattered throughout the stem
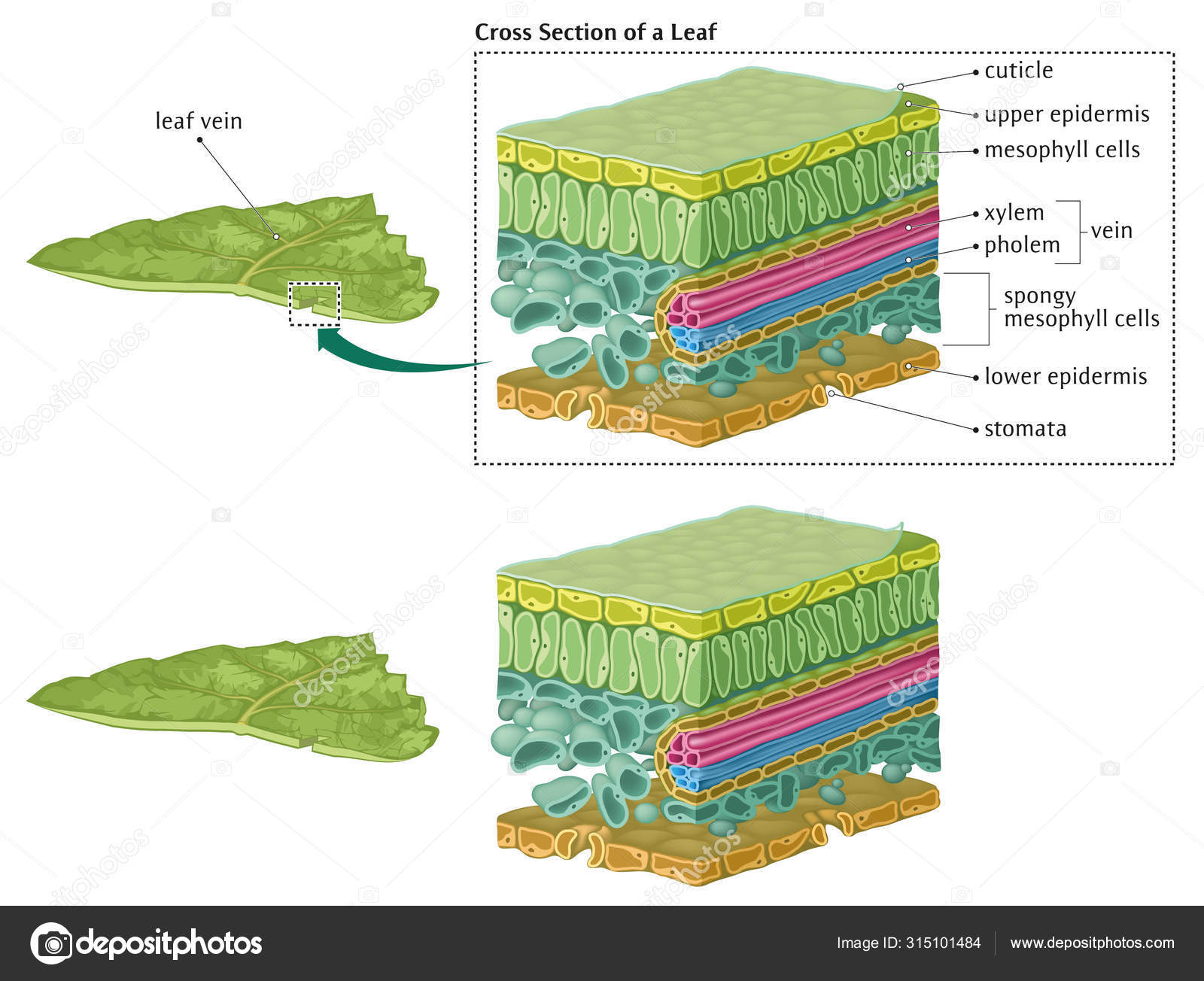
Cross Section Of A Dicotyledonous Leaf Cross section of a dicotyledonous leaf. How to draw the diagram of cross section of a leaf class x. Anatomy of a dicot leaf sunflower leaf. The epidermis consists of a single layer of cells and is the outermost layer of the stem. If a plant has a 1 seed leaf or cotyledon we call it a monocotyledon or monocot for short.
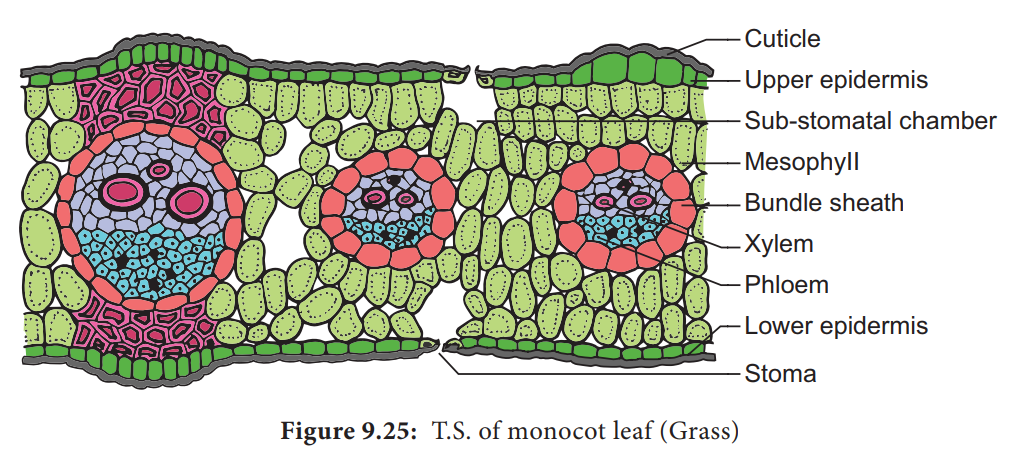
Anatomy of Monocot Leaves | Botany - Biology Discussion ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the anatomy of Zea mays and Triticum monocot leaves. 1. Anatomy of Zea mays - Leaf (Family - Graminae): T. S. reveals the following structures: Epidermis: ADVERTISEMENTS: 1. A single layer is present on the upper as well as lower surfaces of the leaf. 2. Both the […]
18 Major Difference Between Monocot And Dicot Leaf (With ... Monocot Leaf Diagram Characteristics Of monocot Leaf The guard cells of stomata are dumb-bell shaped in monocot leaf. The monocot leaf is slender and long in shape. The epidermal cells have almost straight lateral walls. The orientation of a monocot leaf can be described as isobilateral.
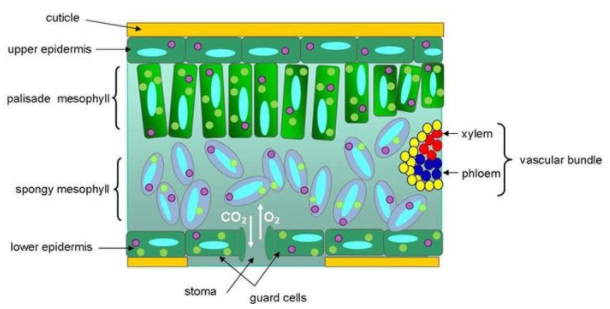
Monocot and Dicot Leaves - Visible Body Leaf dermal tissue. Both monocot and dicot leaves have an outer, waxy layer called the cuticle that covers the dermal tissue of the upper and lower epidermis. The cuticle protects the leaf and helps it retain water. The epidermis, which is located beneath the cuticle, also protects the leaf.
study.com › academy › lessonMonocot: Definition, Function & Examples - Video & Lesson ... Aug 29, 2021 · A monocot is a plant with one seed leaf, referred to as cotyledon. Learn the more extensive definition of monocot through exploring examples of cotyledon and its function in the ecological system.
Stem Anatomy || Monocot and Dicot Stem Cross Section In this tutorial, we have described Stem Anatomy (Monocot and Dicot Stem Cross Section). DICOT STEM CROSS SECTION For studying the internal structure of a typical dicot stem, the stem cross section of a young Sunflower or Cucurbita is taken. A thin transverse section of the stem reveals the following structures under the microscope: 1. Epidermis It forms a single and the outermost layer of the ...
Explore the Difference Between Monocot and Dicot leaf Difference Between Monocot Leaf and Dicot Leaf Historically, plants are classified into two categories based on the number of cotyledons or embryonic leaves. Therefore, the term "monocot" refers to the flowering plants that contain only one cotyledon.





















Comments
Post a Comment