41 ray diagram for nearsightedness
Make a ray diagram to show how the eye defect myopia is corrected by using a suitable lens. Fig. Myopic and its correction. 4216 Views ... 1 Aug 2020 — What is the myopia (near sightedness) ? Draw a ray diagram to show how it can be corrected using a lens.
As we know, from the reference for countless ray diagrams describing the functioning of the eye, when the light suffers higher refraction than the usual the eye would not be able to form an image for faraway objects. Myopia Causes. Hereditary is one of the natural factors for a person to have the defect of myopia.

Ray diagram for nearsightedness
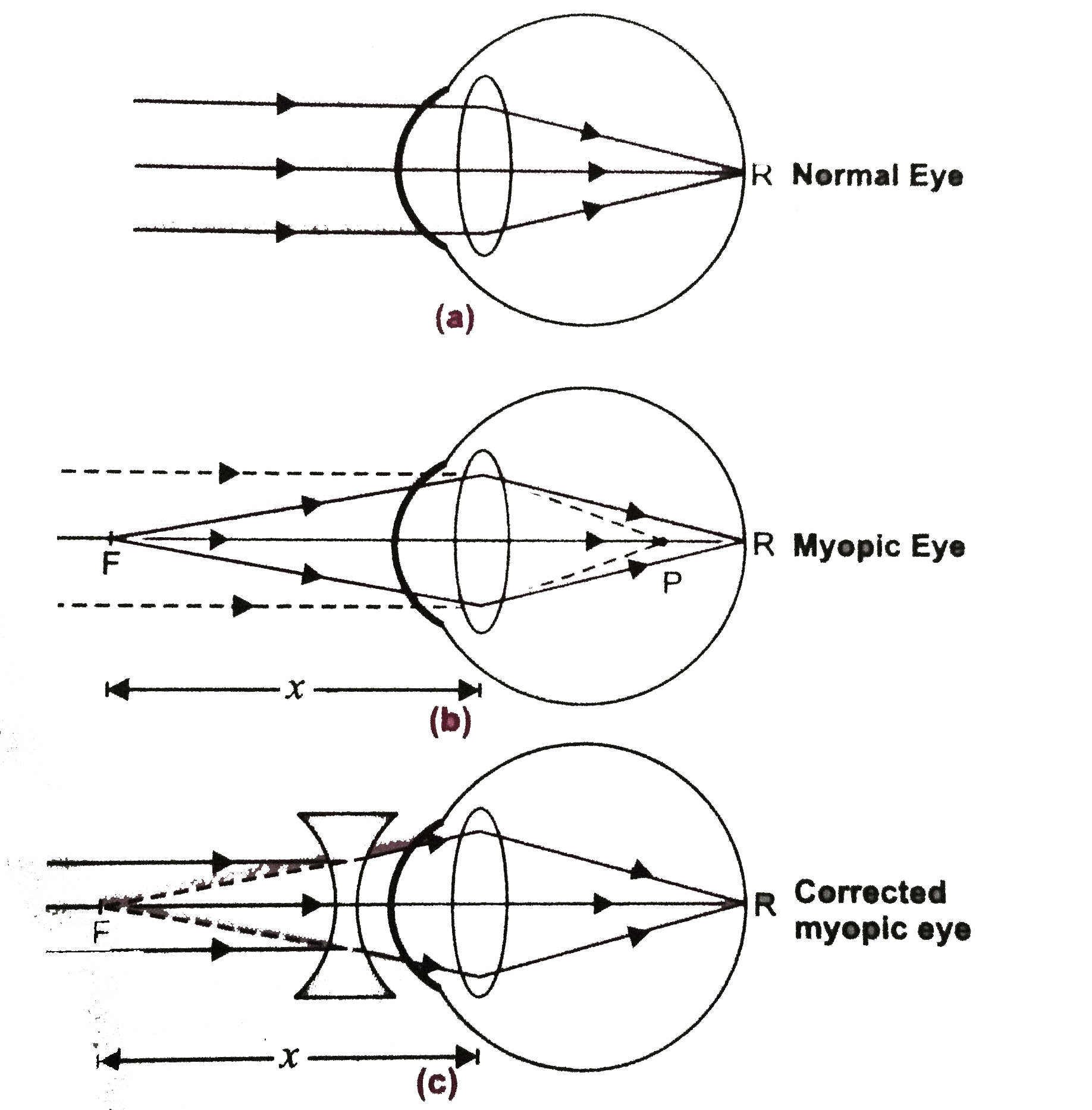
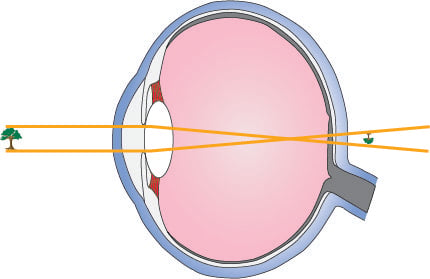
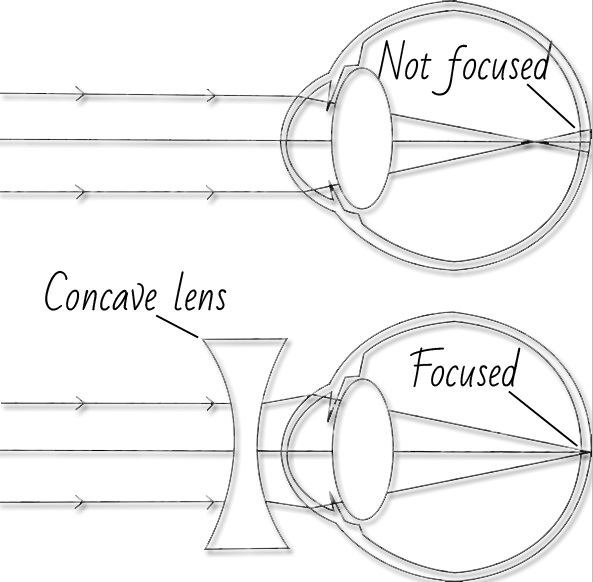
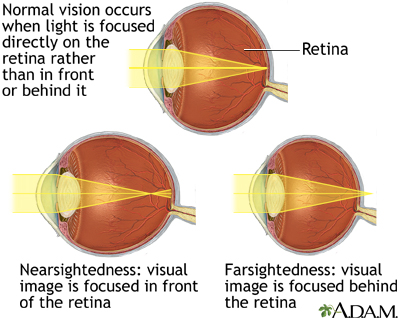
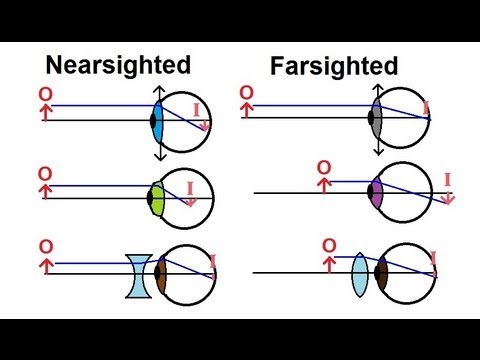
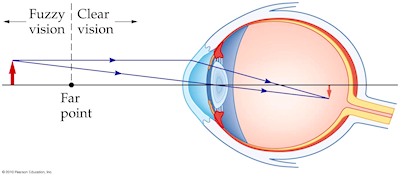
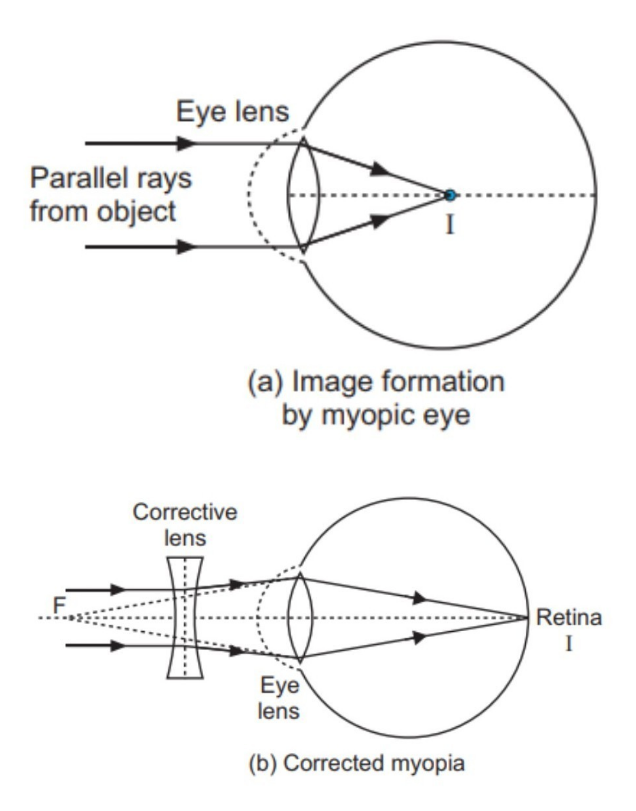
Since the nearsighted eye over converges light rays, the correction for nearsightedness is to place a diverging spectacle lens in front of the eye. This reduces ... Answer. . Myopia is also known as nearsightedness, which occurs when the eyeball is too long so it affects how the cornea and lens focus. This causes light rays to focus at a point in front of the retina , rather than directly on its surface. For, the correction of it , a concave lens is used. A concave lens causes light rays to diverge before they strike the lens of the eye so that the image is formed on the retina. The human eye's ability to accommodate allows it to view focused images of both nearby and distant objects. As mentioned earlier in Lesson 6, the lens of the eye assumes a large curvature (short focal length) to bring nearby objects into focus and a flatter shape (long focal length) to bring a distant object into focus. Unfortunately, the eye's inability a wide variance in focal length leads to a variety of vision defects. Most often, the defect occurs at one end of the spectrum - either the inability to assume a short focal length and focus on nearby objects or the inability to assume a long focal length and thus focus on distant objects. Nearsightedness or myopia is the inability of the eye to focus on distant objects. The nearsighted eye has no difficulty viewing nearby objects. But the ability to view distant objects requires that the light be refracted less. Nearsightedness will result if the light from distant objects is refracted more than is necessary. The problem is most common as a youth, and is usu
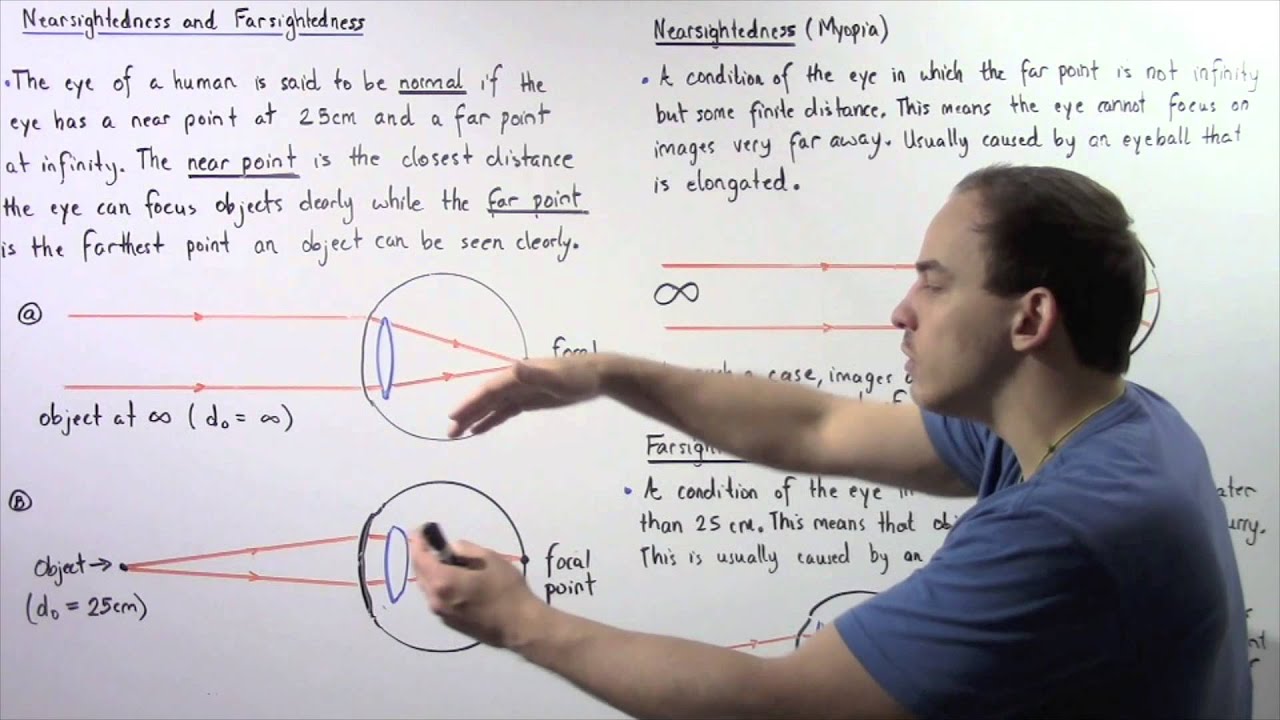
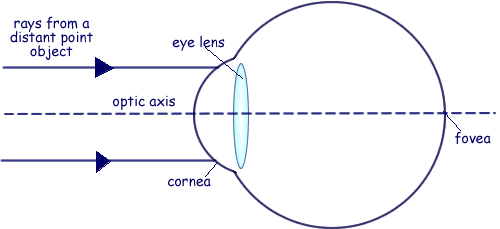
Ray diagram for nearsightedness. Myopia or short sightedness is the defect in which person is unable to focus far off objects clearly. This happens as the eye is unable to relax its eye ... Draw ray diagrams each showing (i) myopic eye and (ii) hypermetropic eye. Answer. Verified. 113.1k + views. Hint: Myopia is an eye disorder and commonly known as near-sightedness and it is otherwise known as short-sightedness. In myopia, the affected person can see the close object clearly, but the far object is blurry. Refractive conditionsrefers to all the conditions that require us to wear glasses. The word refractionrefers to what happens to light when it passes through lenses. Since the cornea acts like a lens, it can be said that the cornea refractslight. I will continue to use the term ‘refract’ in the appropriate contexts, but whenever I do, you can pretty much replace that word in your head with the word ‘focus’ and you won’t miss a beat. As we learned in Lesson 5, if the light is refracted such that it becomes perfectly focused on the retina, clear vision will be produced. However, if the light entering the eyes is not refracted perfectly onto the retina, vision will be blurry and the eye is said to have a refractive condition. (I.e., a focusing condition) The 3 main refractive conditions are: 1. nearsightedness (myopia) 2. farsightedness (hyperopia) 3. astigmatism The lack of a refractive condition is called emmetropia. ... draw a ray diagram that illustrates qualitatively how nearsighted or farsighted vision can be corrected (students do not need to draw exact ray diagrams ...
Aug 05, 2017 · A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens. Start studying chapter 30 and 31. Nearsightedness And Its Correction Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people. All of the above the wavy bright and dark lines at the bottom of a swimming pool are the result of the water surface behaving like moving. 12 nearsighted people wear glasses whose lenses are diverging. The human eye's ability to accommodate allows it to view focused images of both nearby and distant objects. As mentioned earlier in Lesson 6, the lens of the eye assumes a large curvature (short focal length) to bring nearby objects into focus and a flatter shape (long focal length) to bring a distant object into focus. Unfortunately, the eye's inability a wide variance in focal length leads to a variety of vision defects. Most often, the defect occurs at one end of the spectrum - either the inability to assume a short focal length and focus on nearby objects or the inability to assume a long focal length and thus focus on distant objects. Nearsightedness or myopia is the inability of the eye to focus on distant objects. The nearsighted eye has no difficulty viewing nearby objects. But the ability to view distant objects requires that the light be refracted less. Nearsightedness will result if the light from distant objects is refracted more than is necessary. The problem is most common as a youth, and is usu Answer. . Myopia is also known as nearsightedness, which occurs when the eyeball is too long so it affects how the cornea and lens focus. This causes light rays to focus at a point in front of the retina , rather than directly on its surface. For, the correction of it , a concave lens is used. A concave lens causes light rays to diverge before they strike the lens of the eye so that the image is formed on the retina. Since the nearsighted eye over converges light rays, the correction for nearsightedness is to place a diverging spectacle lens in front of the eye. This reduces ...

What Is Myopia Near Sightedness Draw A Ray Diagram To Show How Is Can Be Corrected Using A Lens Brainly In
What Is Myopia State The Two Causes Of Myopia With The Help Of Labelled Ray Diagrams Show Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
How Do We See An Object Using Spectacles When We Don T Actually See The Object Rather We See A Virtual Smaller Version Of It We See The Object Clearly But Don T See

Myopia Correction Diagram How To Draw Myopia Correction Diagram Myopic Eye Diagram Science Dia Youtube

State Two Main Causes Of A Person Developing Near Sightedness With The Help Of A Ray Diagram Suggest How He Can Be Helped To Overcome This Disability Snapsolve
A Student Sitting At The Back Of The Classroom Cannot Read Clearly The Letters Written On The Blackward What Advice Will A Doctor Give To Her Draw Ray Diagram For The

A A Student Suffering From Myopia Is Not Able To See Distinctly The Objects Placed Beyond 5 M List Two Possible Reasons Due To Which This Defect Of Vision May Have
A Person Suffering From Hypermetropia Wants To Read His Book Should He Increase Or Decrease The Distance Quora
Describe With A Ray Diagram How A Person With Myopia Can Be Helped By Spectacles 2005 Cbse Physic Class 10



















Comments
Post a Comment