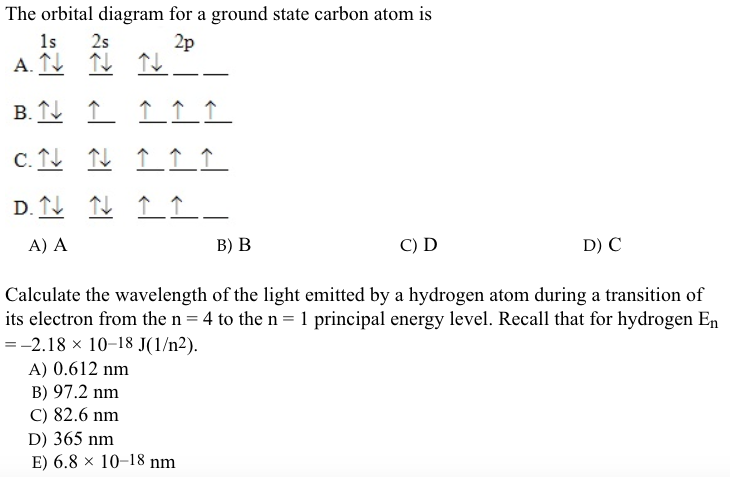
42 carbon orbital diagram
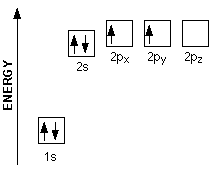
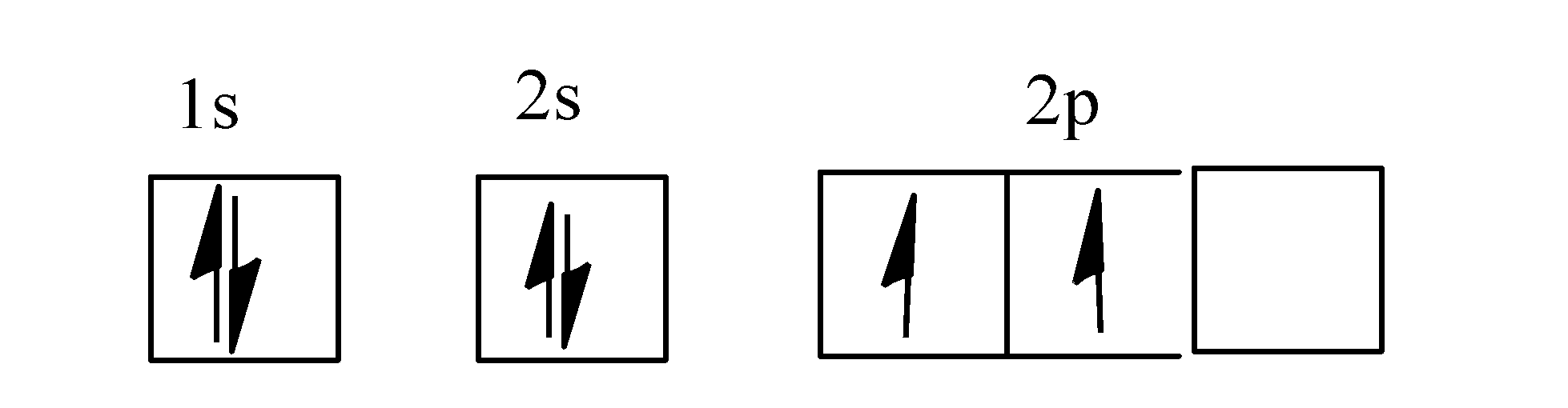
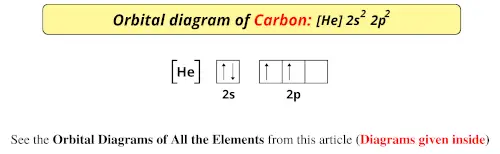
Aug 27, 2017 · The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is #2# , each with opposite spins (Pauli's exclusion principle). In a neutral carbon atom, the #"1s"# sublevel has one orbital with two electrons with opposite spins, represented by the arrows pointing in opposite directions. What is the orbital notation of carbon? Carbon has 6 protons and electrons, so it has 2 in the 1S orbital, 2 in the 2S orbital, and 2 in the 1P orbital. This is often expressed as [HE]2S2 2Ps, because it has the same configuration as helium plus 4 additional electrons whose positions are shown after the bracketed element.
Feb 20, 2021 · The element carbon has 6 electrons in total and one of the main things that many users might not know is the symbol by which it is represented. The symbol of carbon is written as 6. Carbon Electron Dot Diagram. If we talked about the electronic configuration of the element then, carbon is an element whose electronic configuration is given as 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2.
Carbon orbital diagram
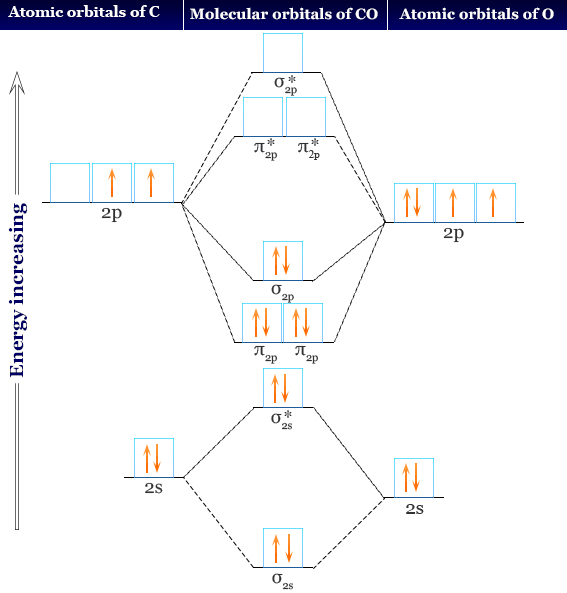
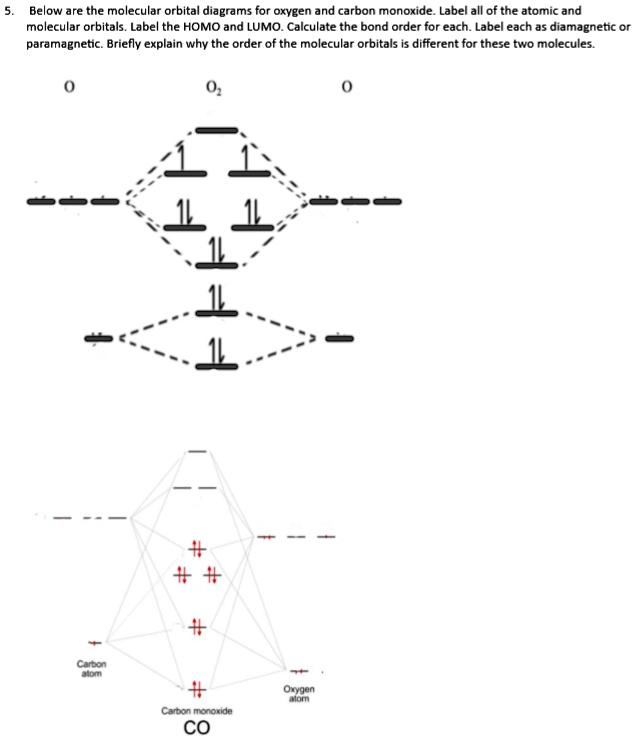
What Is The Correct Orbital Diagram For Carbon? The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is 2, each with opposite spins … Table of Contents How to write an orbital diagram for CO2 +? How are electrons arranged in an orbital diagram? A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Likewise, the left side has AO's of oxygen. And in the middle is the MO. Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene
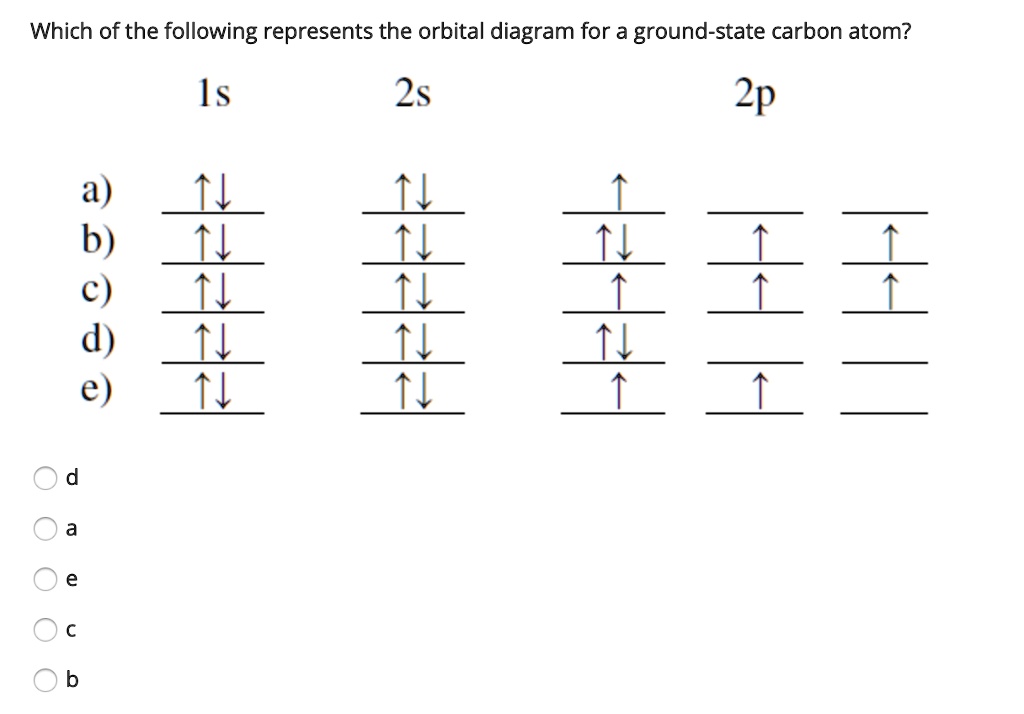
Carbon orbital diagram. Apr 06, 2019 · Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. The Pauli Exclusion Principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital. I am fairly sure the first diagram I drew for carbon dioxide is wrong in terms of showing π bonding. Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Molecule Video Lecture from Chapter Nature of Chemical Bond of Subject Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSE & NEET.W... Carbon is the sixth element with a total of 6 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for carbon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for C goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining two electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the C electron configuration will be ... 8 May 2021 — By Hund's rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s2 2s2 2p2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c.
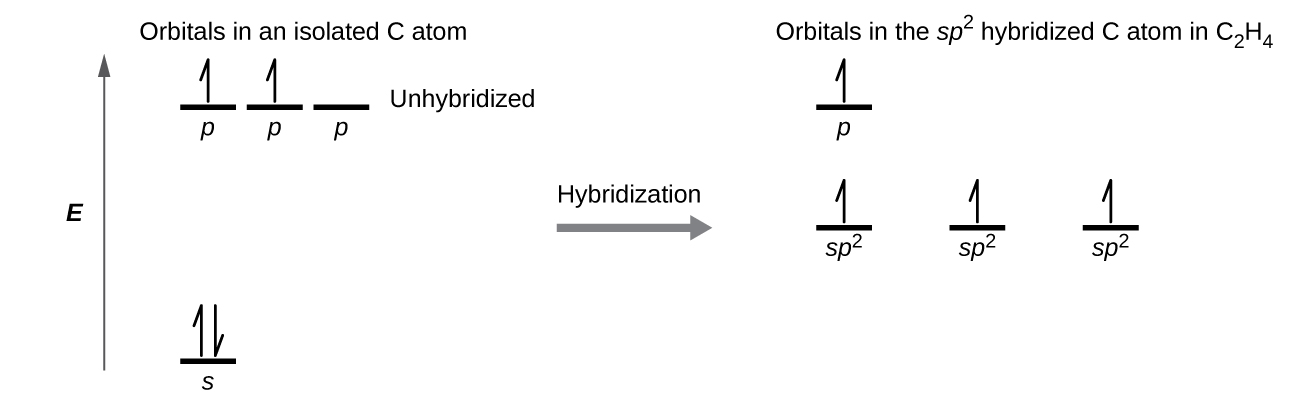
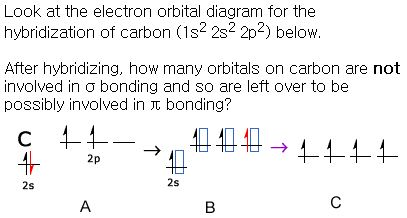
There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of carbon and 6.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. The angular overlap diagrams for the molecular orbitals with high d orbital .. For Co2+: High-spin octahedral d7 has LFSE = -∆o. Tetrahedral d7 has. As it is sometimes explained, the statement that 4 s orbital is lower in energy than 3 d But while you fill 3 d orbital with electrons it becomes lower and lower in. Part B. Draw the orbital ... According to the Bohr diagram of Carbon, the outer shell is L-shell which contains 4 valence electrons. Properties of Carbon It belongs to Group 14 and period 2 in the periodic table. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent in nature. It has an electronegativity of 2.55 according to the Pauling scale. The common oxidation state of carbon is +4 and +2. Write The Orbital Diagram Of Carbon Before Sp3 Step 1. 1 of 2. let us draw orbital diagram to represent the electron configuration of carbon before and after s p 3 sp^3 s p 3 hybridization. the valence electron configuration: 2 s 2, 2 p 2 2s^2, 2p^2 2 s 2, 2 p 2. when we assign electrons to the orbitals of the same energy, we first fill the orbitals with one electron each with same spin.
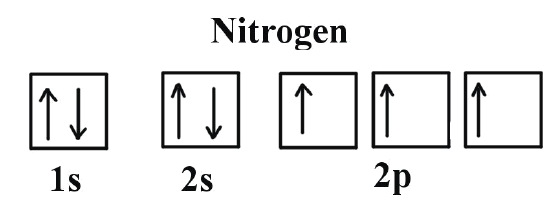
Its full orbital diagram is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6. STEEL and Fe-C PHASE DIAGRAM 22. An Fe-C alloy with 0.395 weight % carbon is austenitized at 1000 C and very slowly cooled to 728 C. What is the amount (weight percent) of austenite present in the microstructure at 728 C? (A) 25 (B) 40 (C) 50 (D) 100. Orbital diagram of fe. By Hund's rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s2 2s2 2p2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c. Experimentally, it is found that the ground state of a neutral carbon atom does indeed contain two unpaired electrons. Draw an orbital diagram for nitrogen, Z = 7. Orbital Diagram of Carbon Study Chemistry, Chemistry Worksheets, Chemistry Classroom, Chemistry Humor,. Elizabeth Mayhew. 127 followers. More information. Jul 01, 2021 · Electron configuration of carbon (C) atom through orbital diagram Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
Co3+ orbital diagram Transcribed image text: Draw an orbital diagram for the Zn2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ ions in the presence of solvent molecules. Use up and down arrows to represent the spin of electrons.
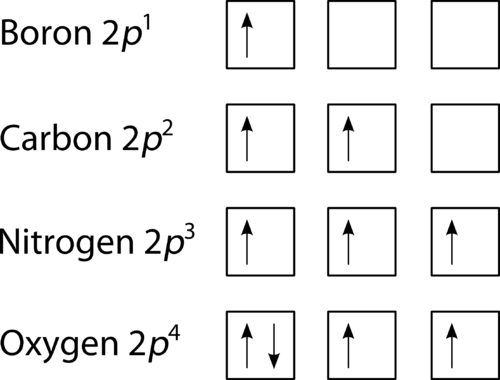
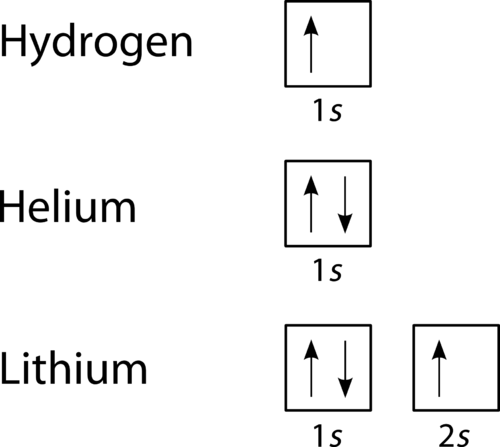
Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals.
The filling diagram for carbon is shown in the Figure below. There are two 2 p electrons for carbon and each occupies its own 2 p orbital. Electron filling ...
Molecular Orbitals for CO. Jmol models of wavefunctions calculated at the RHF/3-21G* level. To view a model, click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown The results displayed may be switched between those from a low level of calculation and those from a high level.
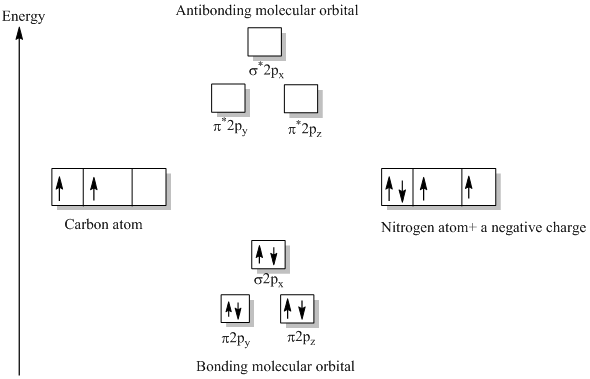
What is molecular orbital diagram of CO? Carbon monoxide MO diagram. Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The valence molecular orbitals in both atoms are the 2s and 2p orbitals. The molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide (Figure 5.3. Is there SP mixing in CO?
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Polyatomic CO2 Molecules - Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structures - YouTube. Carbon dioxide (CO2), molecule is triatomic and linear like Beryllium di hydride (BeH2 ...
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
Some corrections from previous video.. Sorry for the unintentional mistakes i made. So here is the correct one ok.
Both s and p orbitals of O are coloured black on the diagram. Both contribute to some extent to all of the σ MOs, though only the more important correlation lines are marked in. For a further exploration of sp mixing, see Molecular Orbitals for CO
Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene
A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Likewise, the left side has AO's of oxygen. And in the middle is the MO.
What Is The Correct Orbital Diagram For Carbon? The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is 2, each with opposite spins … Table of Contents How to write an orbital diagram for CO2 +? How are electrons arranged in an orbital diagram?

















Comments
Post a Comment