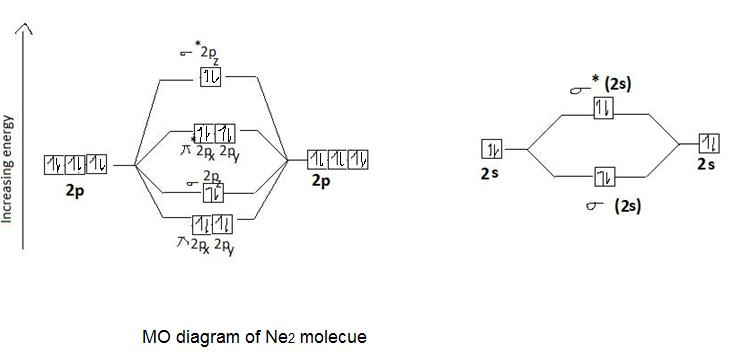
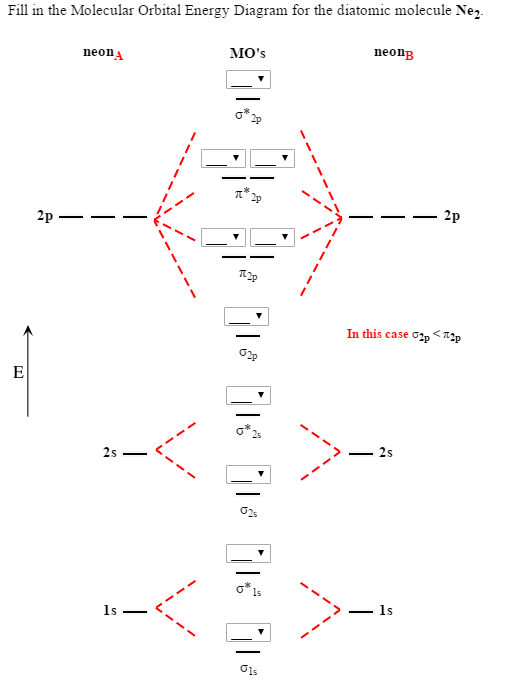
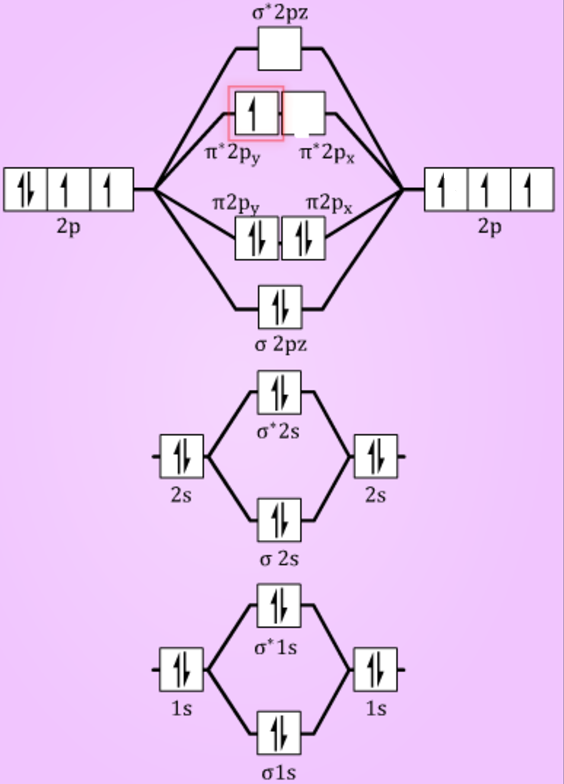
43 ne2 mo diagram
Mar 17, 2019 · Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.Draw the molecular orbital diagram for Ne 2 + and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable. Answer: Question: Is Ne2 2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? To understand this answer you have to know about molecular orbital (MO) theory of bonding. You can learn about it and its application to 2nd row elements here: The Central Science, Chapter 9, Section 8 Within that document is this diagram...
Mar 4, 2018 — Molecular orbital diagram of · Neon atom has 10 electrons and its electronic configuration is . When molecule is considered, it has two neon ...2 answers · 19 votes: Bond order of Ne2 = (10-10) =0 So Ne2 is unstable ;Ne2 cannot exist

Ne2 mo diagram
Problem 1. After reading the theory part draw the MO diagrams for the following diatomic omonuclear molecules: H2, B2, C2, N2, O2, Ne2, F2.13 pages Feb 03, 2019 · There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc) . One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen. The correlation diagrams for nitrogen and carbon monoxide and the first are nearly parallel to the corresponding orbital energy curves. Bond order for N2 is 3; bond order for N2- is and bond ... Answer (1 of 4): Neon is denoted by Ne which is noble gas. Noble gases are non-reactive by nature.The outermost shell in Ne element is fully filled with electrons where the electron is 10 in number. This means that will have 20 electrons. This is why it does not need to react with any other atom ...
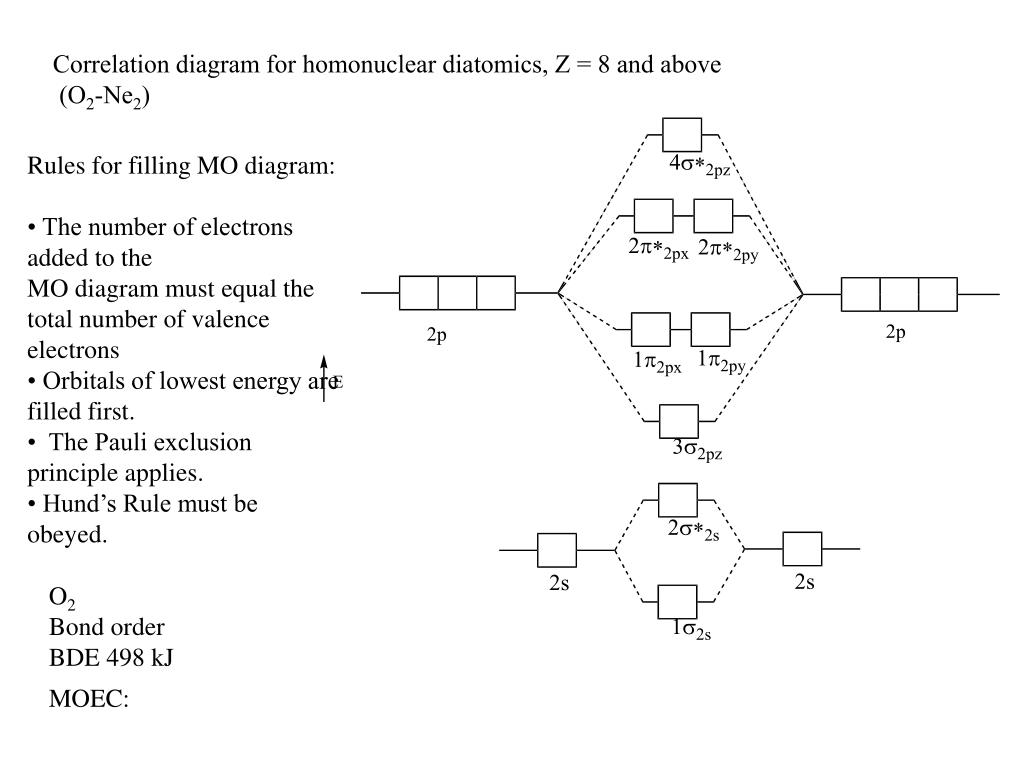
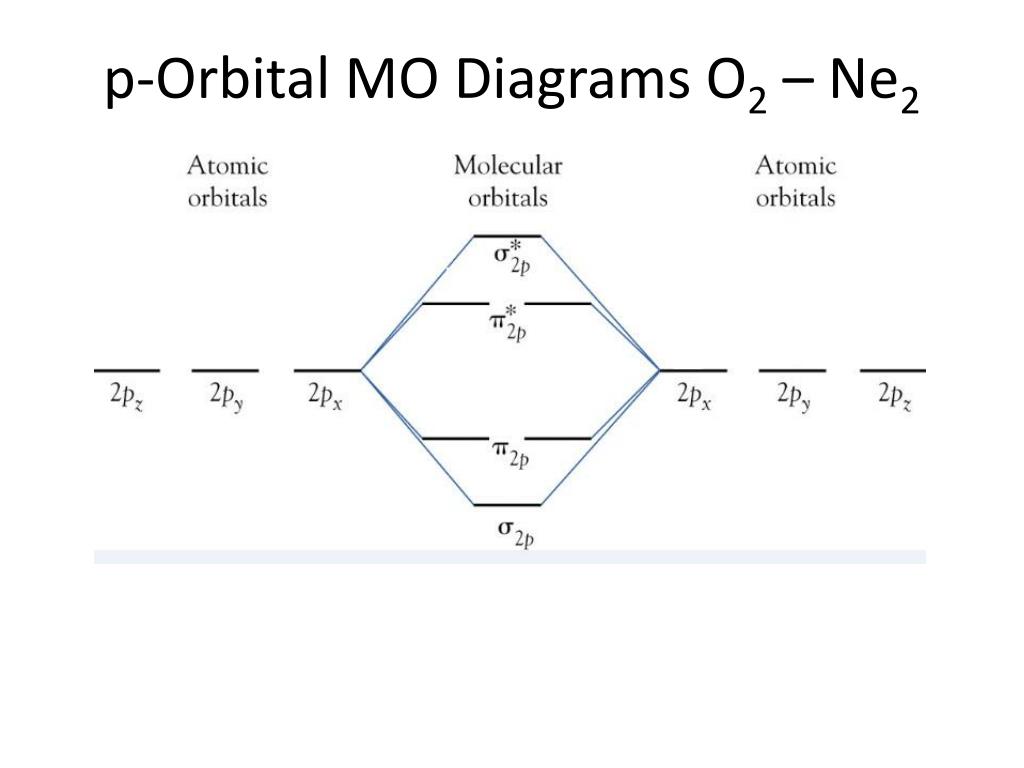
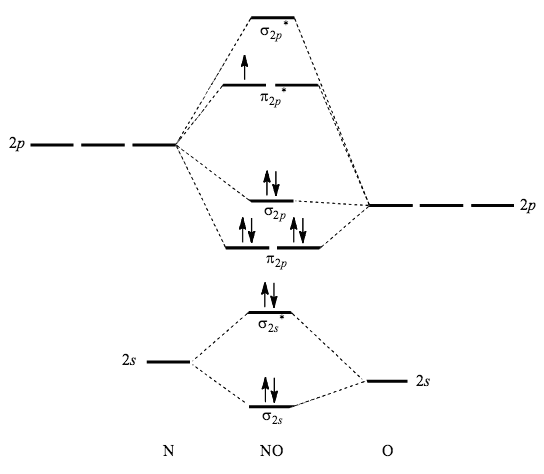
Ne2 mo diagram. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown below to determine which of the following molecules/species is most stable (O2, F2 and Ne2) . Explain their magnetic ... The bond order is Figure The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the ... the pi(2p) bonding orbitals are LOWER than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.N2(2-) has a bonding order of 2, which predicts that there will be a stable double ... A molecular orbital diagram or MO diagram for short is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the Linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method (LCAO method) in particular .This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen and carbon monoxide but becomes ...
Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the Ne2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons. Energy ; Question: O STRUCTURE AND BONDING Drawing the MO energy diagram for a Period 2 homodiat... Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the Ne2 molecule. If the M.O. diagram is drawn it is seen that no. Of bonding orbitals = no. Of antibonding orbitals. Bond order = no. Of bonds = B.Os ...4 answers · 5 votes: Molecular orbital confuguration of Ne2 is σ1s²σ*1s²σ2s²σ*2s²σ2Pz²π2Px²π2Py²π*2Px²π ... Dec 30, 2018 · Ne2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. This Videos are recorded in live lectures by 20 years experienced Chemistry teacher, to help students to understand concepts in much better. Answer to For Ne2, construct three molecular orbital diagrams, one each for the neutral molecule, the +1 cation, and the -1 anion. According to Molecular Orbital theory, only ... For Ne2, construct three molecular orbital diagrams, one each for the neutral molecule, the +1 cation, and the -1 anion. Give each MO an appropriate label. Determine the electron configuration and bond order for each, and rank the three species in order of increasing bond order. Rationalize the trend in bond order in terms of bond strength.
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration. Answer (1 of 3): Here is the MO diagram for O₂: Whilst this is the MO diagram for N₂: If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the Second Period (Li₂, Be₂, B₂, C₂, N₂, O₂, and F₂), the resulting pattern looks like this: When it comes to O₂ and N₂, I think there are two things ... Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Page 1. MO Diagrams for Elements Li2 through Ne2. (Don't memorize.) Li2 through N2. O2 through Ne2. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 .
Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 . Bond order = [(number of bonding electon â number of antibonding electron)/2] Now, for N2â it is 2.5 See the MO diagram of N2â It is defined as the heat of formation for ions of opposite charge in the gas phase to combine into an ionic solid. The graphical representation presented in Fig.
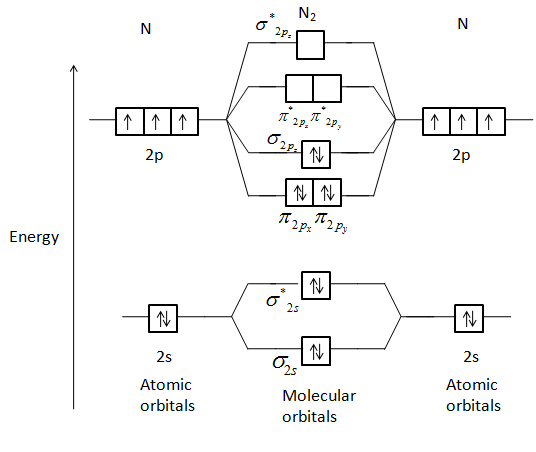
Show activity on this post. I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For N X 2 the orbitals in increasing energy are: σ 1 s < σ 1 s ∗ < σ 2 s < σ 2 s ∗ < π 2 p x, π 2 p y < σ 2 p z < π 2 p x ∗, π 2 p y ∗ < σ 2 p z ∗ ...
2p 2s mo diagram for n2 n2, o2, f2, ne2? Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas ( 1 ion) (n2( )). The mos for the valence orbitals of the second period are shown in figure 12. The molecular orbital diagram shows the creation and filling of mos in a bond.
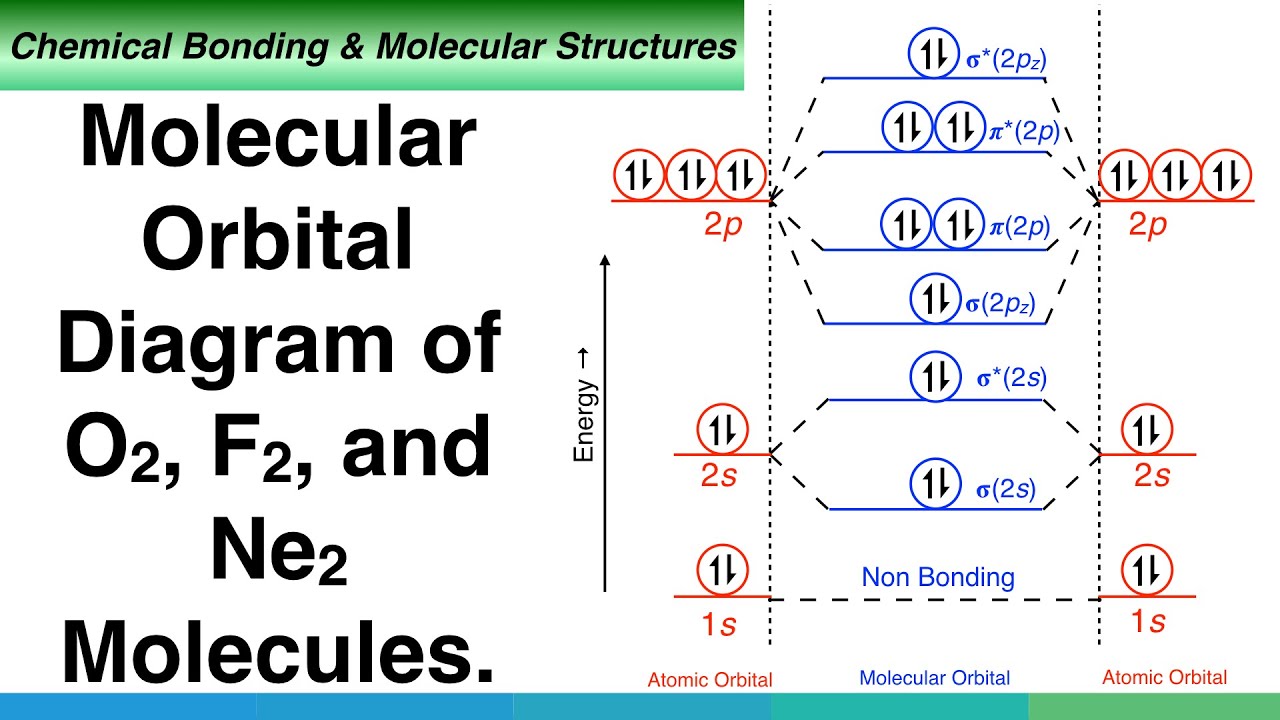
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d...
Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: What is the bond order for F2? 1 Is F2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for F2-? Is F2- paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for F2+? Is F2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Which of the three has the longest bond? Which of the three has the ...
Molecular Orbital Theory: The molecular orbital theory is based on the idea that when two atomic orbitals of similar energy and symmetry overlap, they combine to form a molecular orbital.
FREE Expert Solution. We are asked to determine the bond order from the molecular orbital diagram of Ne2 and to check whether the calculated bond order agrees with the Lewis structure of Ne2. Part A. Draw the Lewis Structure of Ne2. Part B. Determine the bond order from the molecular orbital diagram of Ne2.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular orbital theory helps Chapter 9 Section 6 Molecular orbital theory helps you predict several important properties of the substance. Bond order (bond length and bond strength). Bond enthalpy (bond energy) Dr. A. Al-Saadi 22 Magnetic properties. MO diagram of O 2
4 answersSo here we're looking at the molecular orbital theory to describe bonding. ... Calculate the bond order of Ne2 and determine if you would expect this ...
MO diagram for 02, F2, Ne2 02p 02s MO AO Õ2p 02s MO AO D 2s AO L Qcoiunð@ (d) IÒe- MO diagram for B2, C2, TT*2p MO diagram for 02, F2, Ne2 AO AO TT2p: 02s MO AO -Ÿoac\ order - 02p TT2p MO D AO Œ2S . Title: Discussion Sheet 11 KEY.pdf Created Date:
This phenomenon is explained by s-p mixing. All the elements in the second period before oxygen have the difference in energy between the 2s and 2p orbital small enough, so that s-p mixing (combination) can occur lowering the energy of the σ(2s) and σ*(2s) and increasing the energy of the σ(2p) and σ*(2p) molecular orbitals.
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
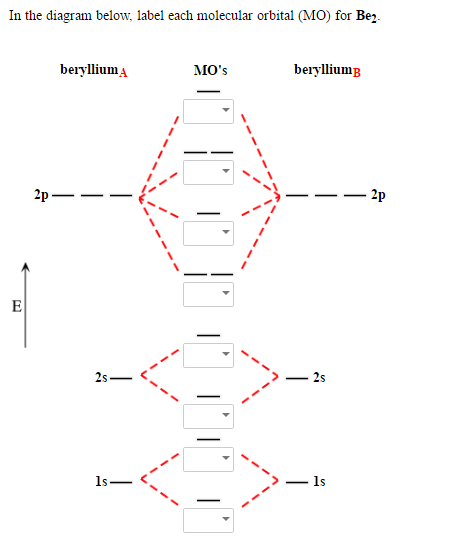
In He2 (dihelium), the two 1s atomic orbitals overlap to create two molecular orbitals: sigma(1s) and sigma(1s)*. You fill these molecular orbitals with the...
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
The diagram above is the molecular.Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules Introduction: In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.
#3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron.
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical Since molecular oxygen contains two electrons in an antibonding orbital, it might be possible to This page from Imperial College (London) has MO diagrams for molecules such as ethane, ethylene, and water.
Answer (1 of 4): Neon is denoted by Ne which is noble gas. Noble gases are non-reactive by nature.The outermost shell in Ne element is fully filled with electrons where the electron is 10 in number. This means that will have 20 electrons. This is why it does not need to react with any other atom ...
Feb 03, 2019 · There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc) . One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen. The correlation diagrams for nitrogen and carbon monoxide and the first are nearly parallel to the corresponding orbital energy curves. Bond order for N2 is 3; bond order for N2- is and bond ...
Problem 1. After reading the theory part draw the MO diagrams for the following diatomic omonuclear molecules: H2, B2, C2, N2, O2, Ne2, F2.13 pages























Comments
Post a Comment